1.3 Food Guide Pyramid (1).pdf 6h2y4v
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View 1.3 Food Guide Pyramid (1).pdf as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 1,473
- Pages: 47
FST 307 BASIC NUTRITION CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC NUTRITION
CHAPTER OUTCOMES At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:a) Explain briefly about diet planning principles, Malaysia dietary guidelines and food guide pyramids b) Describe briefly about dietary reference intake.
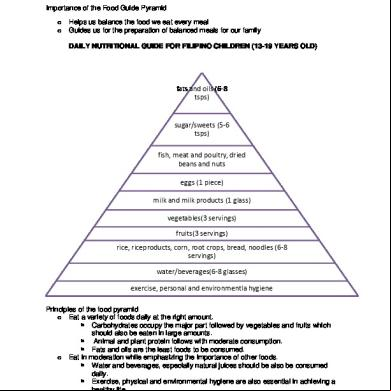
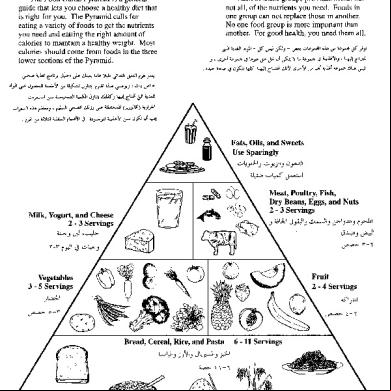
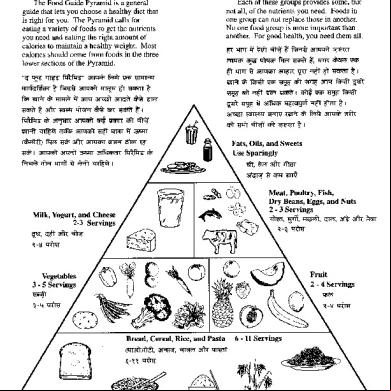
FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID a) Graphic device that serves as a guide for planning diets that meet nutritional requirements, promote health and as a device for making daily food choices b) Food guide pyramids are broken down into food groups of differing nutritional value c) They illustrate the relative contribution each food
group should make in the diet
d) Lists types of food rather than directions on what to eat e) Encourages you to decide on foods to fit you best f) Healthy diets consist of foods from all of the groups
g) Consists of five food groups and ranges of daily servings
FOOD GROUPS PRESENTED IN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID 1. Bread, Cereal, Rice, Pasta, etc. 2. Fruits 3. Vegetables 4. Milk, Yogurt, Cheese, etc. 5. Meat, Poultry, Fish, Beans, Eggs, and Nuts
6. Fats, oils and sweets a) Added for enhancement of flavor and texture b) They not a food group c) Included because of the significant calories they
often contribute
MALAYSIAN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
NEW MALAYSIAN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
One Serving Equals …
1 slice of wholemeal bread ½ cup cooked rice ½ cup soaked bihun, mee or pasta ½ side-plate-sized capati 1 cup plain rice porridge ½ cup ready-to-eat breakfast cereal 1 medium-sized potato 3 plain biscuits
2 servings
One Serving Equals …
½ medium-sized guava 1 small to medium whole orange, pear or apple 1 medium-sized banana 1 slice papaya, pineapple, watermelon
3 servings
One Serving Equals … ½ cup cooked dark green leafy vegetables with edible stems ½ cup cooked fruit or root vegetables
One Serving Equals …
1 glass of milk 1 cup yoghurt 1 slice cheese
½ - 2 servings of poultry, meat, egg 1 serving of fish ½ - 1 serving of legumes
One Serving Equals …
1 medium-sized chicken drumstick 1 medium-sized ikan kembong 2 matchbox-sized lean meat 5 dessert spoon headless ikan bilis Note: One (1) matchbox lean meat = 1 piece tempeh = 1 hard taukua = 2 dsp peanut butter = ½ cup dried legumes/beans = 4 dsp shelled small prawns
Tip is not a group, but about fats and sweets These foods given smallest area, saying that fat, oils, and sweets should be small part of our diet The more types of food you eat in a day, the wider the array of nutrients and other beneficial components of food you get We consume 18 to 20 different foods a day Dietary guidelines developed for Japan recommend people eat 30 different foods daily
UNBALANCE DIET
DAILY FOOD GUIDE Perceptions and actual intakes
UNITED STATES FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
SONIC BOOM 1
PORTION SIZES
PORTION SIZES a) A portion is different than a serving b) Portion size of pasta in restaurants is 3 cups = 6
standard servings of pasta c) Larger
portions increase sales encourage people to eat more
volume
and
d) Rising rates of obesity may be in part related to increased portion size
FOOD PLAN IN ACTION
MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES
MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES 1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Enjoy a variety of foods Maintain a healthy body weight by balancing food intake with regular physical activity Eat more rice and other cereal products, legumes, fruits and vegetables Minimize fat in food preparation and choose foods that are low in fat and cholesterol Use salt sparingly and choose foods low in salt Reduce sugar intake and choose foods low in sugar Drink plenty of water daily Practice and promote breastfeeding
NEW MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES Eat a variety of foods within your recommended intake Maintain body weight in a healthy range Be physically active everyday Eat adequate amount of rice, other cereal products (preferably whole grain) and tubes 5. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables everyday 6. Consume moderate amounts of fish, meat, poultry, egg, legumes and nuts 7. Consume adequate amounts of milk and milk products 8. Limit intake of foods high in fats and minimize fats and oils in food preparation 9. Choose and prepare foods with less salt and sauces 10. Consume foods and beverages low in sugar 11. Drink plenty of water daily 12. Practice exclusive breastfeeding from birth until six months and continue to breastfeed until two years of age 13. Consume safe and clean foods and beverages 14. Make effective use of nutrition information on food labels 1. 2. 3. 4.
DIET PLANNING PRINCIPLE 1. Adequacy 2. Balance 3. Calorie (energy) control 4. Variety 5. Moderation
6. Nutrient density 7. Energy density
1. ADEQUACY a) Characterizes a diet that provides all of the essential nutrients, fiber, and energy (calories) in amounts sufficient to maintain health
2. BALANCE a) A feature of a diet that provides a number of types
of foods in balance with one another, such that foods rich in one nutrient do not crowd out of the diet foods that are rich in another nutrient.
b) Provide calories, nutrients, and other components in the right proportion c) Diets that contain too much or too little nutrients are out of balance d) Diets that provide more calories than needed to
maintain a healthy body weight are also out of balance
3. CALORIE (ENERGY) CONTROL a) Control of consumption of energy (calories) b) A feature of a sound diet plan.
4. VARIETY
5. MODERATION
The attribute of a diet that provides no unwanted constituent in excess
6. NUTIRENT DENSITY a) Refers to a food that supplies large amounts of
nutrients relative to the number of calories it contains. b) The higher the level of nutrients and the fewer the number of calories, the more nutrient dense the food is.
7. ENERGY DENSITY a) A measure of the energy of food provides relative to the amount of food
36
SONIC BOOM 2
DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKES
DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKES a) A set of reference values for energy and nutrients
that can be used for planning and assessing diets for healthy people b) DRIs include values for energy, protein, carbohydrates, fats, micronutrients, and other substances of nutritional importance (e.g., phytochemicals). c) DRIs aim to promote health and reduce the incidence of chronic disease, as well as prevent deficiencies.
SET OF VALUES IN DRI 1.
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
2.
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs)
3.
Adequate Intakes (AIs)
4.
Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (ULs)
1. ESTIMATED AVERAGE EQUIREMENT (EAR) a) The amount of a nutrient that is estimated to meet the requirement for the nutrient in half of the people of a specific age and gender.
b) Amount that meets the nutrient requirements of 50% of people in a life stage/gender group c) Based on functional indicator of optimal health d) The EAR is used in setting the RDA
2. RECOMMENDEDDIETARY ALLOWANCE (RDA) a) The average daily amount of a nutrient that is sufficient to meet
the nutrient needs of nearly all (97–98 percent) healthy individuals of a specific age and gender.
b) Amount that meets the needs of most people in a life
stage/gender group
c) The RDA for each nutrient is set at a level at which most people
will not experience a deficiency
3. ADEQUATE INTAKE (AI) a) The average amount of a nutrient that appears to be adequate for individuals when there is not
sufficient scientific research to calculate an RDA.
b) The AI exceeds the EAR and possibly the RDA. c) Amount thought to be adequate for most people
d) AI used when EAR and RDA can’t be determined
4. TOLERABLE UPPER INTAKE LEVEL (UL) a) The maximum amount of a nutrient that is unlikely to pose any risk of adverse health effects to most healthy people. The UL is not intended to be a recommended level of intake. b) The need for setting ULs is the result of more and
more people using large doses of nutrient supplements and the increasing availability of fortified foods.
c) Intake above the UL can be harmful
OTHER DRI a) Estimated energy requirement (EER): the average calorie intake that is predicted to maintain energy balance in a healthy adult of a defined age, gender, weight, height, and level of physical activity, consistent with good health. b) Acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR): a range of intakes for a particular energy source (carbohydrates, fat, protein) that is associated with a reduced risk of chronic disease
while providing adequate intakes of essential nutrients.
PAUSE TO PONDER… a) Can you explain briefly about diet planning principles, Malaysia dietary guidelines and food guide pyramids? b) Ask your friend to describe briefly about dietary reference intake.
SHOCK WAVE
END OF CHAPTER 1.3 FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC NUTRITION
CHAPTER OUTCOMES At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:a) Explain briefly about diet planning principles, Malaysia dietary guidelines and food guide pyramids b) Describe briefly about dietary reference intake.
FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID a) Graphic device that serves as a guide for planning diets that meet nutritional requirements, promote health and as a device for making daily food choices b) Food guide pyramids are broken down into food groups of differing nutritional value c) They illustrate the relative contribution each food
group should make in the diet
d) Lists types of food rather than directions on what to eat e) Encourages you to decide on foods to fit you best f) Healthy diets consist of foods from all of the groups
g) Consists of five food groups and ranges of daily servings
FOOD GROUPS PRESENTED IN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID 1. Bread, Cereal, Rice, Pasta, etc. 2. Fruits 3. Vegetables 4. Milk, Yogurt, Cheese, etc. 5. Meat, Poultry, Fish, Beans, Eggs, and Nuts
6. Fats, oils and sweets a) Added for enhancement of flavor and texture b) They not a food group c) Included because of the significant calories they
often contribute
MALAYSIAN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
NEW MALAYSIAN FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
One Serving Equals …
1 slice of wholemeal bread ½ cup cooked rice ½ cup soaked bihun, mee or pasta ½ side-plate-sized capati 1 cup plain rice porridge ½ cup ready-to-eat breakfast cereal 1 medium-sized potato 3 plain biscuits
2 servings
One Serving Equals …
½ medium-sized guava 1 small to medium whole orange, pear or apple 1 medium-sized banana 1 slice papaya, pineapple, watermelon
3 servings
One Serving Equals … ½ cup cooked dark green leafy vegetables with edible stems ½ cup cooked fruit or root vegetables
One Serving Equals …
1 glass of milk 1 cup yoghurt 1 slice cheese
½ - 2 servings of poultry, meat, egg 1 serving of fish ½ - 1 serving of legumes
One Serving Equals …
1 medium-sized chicken drumstick 1 medium-sized ikan kembong 2 matchbox-sized lean meat 5 dessert spoon headless ikan bilis Note: One (1) matchbox lean meat = 1 piece tempeh = 1 hard taukua = 2 dsp peanut butter = ½ cup dried legumes/beans = 4 dsp shelled small prawns
Tip is not a group, but about fats and sweets These foods given smallest area, saying that fat, oils, and sweets should be small part of our diet The more types of food you eat in a day, the wider the array of nutrients and other beneficial components of food you get We consume 18 to 20 different foods a day Dietary guidelines developed for Japan recommend people eat 30 different foods daily
UNBALANCE DIET
DAILY FOOD GUIDE Perceptions and actual intakes
UNITED STATES FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID
SONIC BOOM 1
PORTION SIZES
PORTION SIZES a) A portion is different than a serving b) Portion size of pasta in restaurants is 3 cups = 6
standard servings of pasta c) Larger
portions increase sales encourage people to eat more
volume
and
d) Rising rates of obesity may be in part related to increased portion size
FOOD PLAN IN ACTION
MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES
MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES 1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
Enjoy a variety of foods Maintain a healthy body weight by balancing food intake with regular physical activity Eat more rice and other cereal products, legumes, fruits and vegetables Minimize fat in food preparation and choose foods that are low in fat and cholesterol Use salt sparingly and choose foods low in salt Reduce sugar intake and choose foods low in sugar Drink plenty of water daily Practice and promote breastfeeding
NEW MALAYSIAN DIETARY GUIDELINES Eat a variety of foods within your recommended intake Maintain body weight in a healthy range Be physically active everyday Eat adequate amount of rice, other cereal products (preferably whole grain) and tubes 5. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables everyday 6. Consume moderate amounts of fish, meat, poultry, egg, legumes and nuts 7. Consume adequate amounts of milk and milk products 8. Limit intake of foods high in fats and minimize fats and oils in food preparation 9. Choose and prepare foods with less salt and sauces 10. Consume foods and beverages low in sugar 11. Drink plenty of water daily 12. Practice exclusive breastfeeding from birth until six months and continue to breastfeed until two years of age 13. Consume safe and clean foods and beverages 14. Make effective use of nutrition information on food labels 1. 2. 3. 4.
DIET PLANNING PRINCIPLE 1. Adequacy 2. Balance 3. Calorie (energy) control 4. Variety 5. Moderation
6. Nutrient density 7. Energy density
1. ADEQUACY a) Characterizes a diet that provides all of the essential nutrients, fiber, and energy (calories) in amounts sufficient to maintain health
2. BALANCE a) A feature of a diet that provides a number of types
of foods in balance with one another, such that foods rich in one nutrient do not crowd out of the diet foods that are rich in another nutrient.
b) Provide calories, nutrients, and other components in the right proportion c) Diets that contain too much or too little nutrients are out of balance d) Diets that provide more calories than needed to
maintain a healthy body weight are also out of balance
3. CALORIE (ENERGY) CONTROL a) Control of consumption of energy (calories) b) A feature of a sound diet plan.
4. VARIETY
5. MODERATION
The attribute of a diet that provides no unwanted constituent in excess
6. NUTIRENT DENSITY a) Refers to a food that supplies large amounts of
nutrients relative to the number of calories it contains. b) The higher the level of nutrients and the fewer the number of calories, the more nutrient dense the food is.
7. ENERGY DENSITY a) A measure of the energy of food provides relative to the amount of food
36
SONIC BOOM 2
DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKES
DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKES a) A set of reference values for energy and nutrients
that can be used for planning and assessing diets for healthy people b) DRIs include values for energy, protein, carbohydrates, fats, micronutrients, and other substances of nutritional importance (e.g., phytochemicals). c) DRIs aim to promote health and reduce the incidence of chronic disease, as well as prevent deficiencies.
SET OF VALUES IN DRI 1.
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
2.
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs)
3.
Adequate Intakes (AIs)
4.
Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (ULs)
1. ESTIMATED AVERAGE EQUIREMENT (EAR) a) The amount of a nutrient that is estimated to meet the requirement for the nutrient in half of the people of a specific age and gender.
b) Amount that meets the nutrient requirements of 50% of people in a life stage/gender group c) Based on functional indicator of optimal health d) The EAR is used in setting the RDA
2. RECOMMENDEDDIETARY ALLOWANCE (RDA) a) The average daily amount of a nutrient that is sufficient to meet
the nutrient needs of nearly all (97–98 percent) healthy individuals of a specific age and gender.
b) Amount that meets the needs of most people in a life
stage/gender group
c) The RDA for each nutrient is set at a level at which most people
will not experience a deficiency
3. ADEQUATE INTAKE (AI) a) The average amount of a nutrient that appears to be adequate for individuals when there is not
sufficient scientific research to calculate an RDA.
b) The AI exceeds the EAR and possibly the RDA. c) Amount thought to be adequate for most people
d) AI used when EAR and RDA can’t be determined
4. TOLERABLE UPPER INTAKE LEVEL (UL) a) The maximum amount of a nutrient that is unlikely to pose any risk of adverse health effects to most healthy people. The UL is not intended to be a recommended level of intake. b) The need for setting ULs is the result of more and
more people using large doses of nutrient supplements and the increasing availability of fortified foods.
c) Intake above the UL can be harmful
OTHER DRI a) Estimated energy requirement (EER): the average calorie intake that is predicted to maintain energy balance in a healthy adult of a defined age, gender, weight, height, and level of physical activity, consistent with good health. b) Acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR): a range of intakes for a particular energy source (carbohydrates, fat, protein) that is associated with a reduced risk of chronic disease
while providing adequate intakes of essential nutrients.
PAUSE TO PONDER… a) Can you explain briefly about diet planning principles, Malaysia dietary guidelines and food guide pyramids? b) Ask your friend to describe briefly about dietary reference intake.
SHOCK WAVE
END OF CHAPTER 1.3 FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID