Benefits Of Fmea m4b4l
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Benefits Of Fmea as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 1,595
- Pages: 9
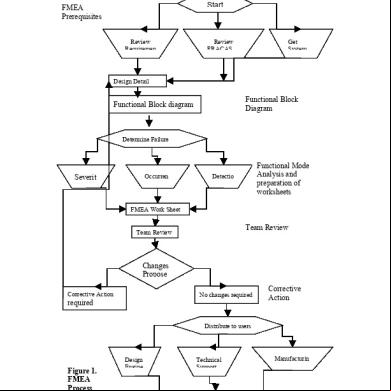
Start
FMEA Prerequisites Review Requiremen
Review FRACAS
Get System
Design Detail
Functional Block Diagram
Functional Block diagram
Determine Failure
Occurren ce
Severit
Functional Mode Analysis and preparation of worksheets
Detectio n
FMEA Work Sheet
Team Review
Team Review
Changes Propose Corrective Action
No changes required
required
Corrective Action
Distribute to s
Figure 1. FMEA Process
Design Engine
Technical
Reliable Equipment s
Manufacturin g
Benefits of FMEA FMEA is designed to assist the engineer improve the quality and reliability of design. Properly used the FMEA provides the engineer several benefits. Among others, these benefits include: •
Improve product/process reliability and quality
•
Increase customer satisfaction
•
Early identification and elimination of potential product/process failure modes
•
Prioritize product/process deficiencies
•
Capture engineering/organization knowledge
•
Emphasizes problem prevention
•
Documents risk and actions taken to reduce risk
•
Provide focus for improved testing and development
•
Minimizes late changes and associated cost
Catalyst for teamwork and idea exchange between functions Team for conducting/reviewing an FMEA – Project Manager – Design Engineer (hardware/software/systems) – Test Engineer – Reliability Engineer – Quality Engineer – Field Service Engineer – Manufacturing/Process Engineer – Safety Engineering Outside supplier engineering and/or manufacturing could be added to the team. Customer representation is recommended if a t development program between /supplier exists.
PURPOSE OF FMEA The purpose of performing an FMEA is to analyze the product's design characteristics relative to the planned manufacturing process and experiment design to ensure that the resultant product meets customer needs and expectations. When potential failure modes are identified, corrective action can be taken to eliminate them or to continually reduce a potential occurrence. The FMEA also documents the rationale for the chosen manufacturing process. It provides for an organized critical analysis of potential failure modes and the associated causes for the system being defined. The technique uses occurrence and detection probabilities in conjunction with severity criteria to develop a risk priority number (RPN) for ranking corrective action considerations.
FMEA's provide the engineer with a tool that can assist in providing reliable, safe, and customer pleasing products and processes. Since FMEA help the engineer identify potential product or process failures, they can use it to: •
Develop product or process requirements that minimize the likelihood of those failures.
•
Evaluate the requirements obtained from the customer or other participants in the design process to ensure that those requirements do not introduce potential failures.
•
Identify design characteristics that contribute to failures and design them out of the system or at least minimize the resulting effects.
•
Develop methods and procedures to develop and test the product/process to ensure that the failures have been successfully eliminated.
•
Track and manage potential risks in the design. Tracking the risks contributes to the development of corporate memory and the success of future products as well.
•
Ensure that any failures that could occur will not injure or seriously impact the customer of the product/process.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis [FMEA] Introduction Customers are placing increased demands on companies for high quality, reliable products. The increasing capabilities and functionality of many products are making it more difficult for manufacturers to maintain the quality and reliability. Traditionally, reliability has been achieved through extensive testing and use of techniques such as probabilistic reliability modeling. These are techniques done in the late stages of development. The challenge is to design in quality and reliability early in the development cycle. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is methodology for analyzing potential reliability problems early in the development cycle where it is easier to take actions to overcome these issues, thereby enhancing reliability through design. FMEA is used to identify potential failure modes, determine their effect on the operation of the product, and identify actions to mitigate the failures. A crucial step is anticipating what might go wrong with a product. While anticipating every failure mode is not possible, the development team should formulate as extensive a list of potential failure modes as possible. The early and consistent use of FMEAs in the design process allows the engineer to design out failures and produce reliable, safe, and customer pleasing products. FMEAs also capture historical information for use in future product improvement. TYPES OF FMEA'S There are several types of FMEAs, some are used much more often than others. FMEAs should always be done whenever failures would mean potential harm or injury to the of the end item being designed. The types of FMEA are: •
System - focuses on global system functions
•
Design - focuses on components and subsystems
•
Process - focuses on manufacturing and assembly processes
•
Service - focuses on service functions
•
Software - focuses on software functions
System FMEA This is used to analyze systems and subsystems in the early concept and design stage. A system FMEA focuses on potential failure modes between the functions of the system caused by system deficiencies. It includes the interactions between systems and elements of the system. The outputs of the system FMEA are •
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of system functions that could detect potential failure modes.
•
A potential list of design actions to eliminate failure modes, safety issues and reduces the occurrence.
The benefits of the system FEMA are that it: •
Helps to select the optimum system alternative.
•
Helps to determine redundancy.
•
Helps to define the basis for system level diagnostic procedures.
•
Increases the likelihood that potential problems will be considered.
•
Identifies potential system failures and their interaction with other systems.
Design FMEA This is used to analyze products before they are released to manufacturing. A design focuses on failure modes caused by design deficiencies. The outputs of the design FMEA are: -
•
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical and / or significant characteristics.
•
A potential list of design actions to eliminate failure modes, safety issues and reduces the occurrence.
•
A potential list of parameters for appropriate testing, inspection, and / or detection methods.
•
A potential list of recommended action for the critical and significant characteristics.
The benefits of design FMEA are that it: •
Establishes a priority for design improvement actions.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
•
Provides information to help through design verification and testing.
•
Helps to identify the critical or significant characteristics.
•
Assists in the evaluation of design requirements and alternatives.
•
Helps to identify and eliminate potential safety concerns.
•
Helps to identify product failure early in the product development phase.
Process FMEA This is used to analyze manufacturing and assembly processes. A process FMEA focuses on failure modes caused by process or assembly deficiencies. The outputs of the process FMEA are: •
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical and/ or significant characteristics.
•
A potential list of recommended actions to address the critical and significant characteristics.
•
A potential list to eliminate the causes of failure modes, reduce their occurrences, and improve defect detection if K cannot be improved.
The benefits of the process FMEA are that it: • Identifies process deficiencies and offers a corrective action plan. •
Identifies the critical and/ or significant characteristics and helps in developing control plans.
•
Establishes a priority of corrective actions.
•
Assists in the analysis of the manufacturing or assembly process.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
Service FMEA This is used to analyze services before they reach the customer. A service FMEA focuses on the failure modes (tasks, errors, mistakes) caused by system or process deficiencies. The outputs of the service FMEA are: •
A potential list of errors ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical or significant tasks, or processes.
•
A potential list of bottleneck processes or tasks.
•
A potential list to eliminate the errors.
•
A potential list of monitoring system / process functions.
The benefits of the service FMEA are that it: •
Assists in the analysis of job flow.
•
Assists in the analysis of the system and/ or process.
•
Identifies task deficiencies.
•
Identifies critical or significant tasks and helps in the development of control plan.
•
Establishes a priority for improvement actions.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
An FMEA program should start •
When new systems, designs, products, processes, or services are designed.
•
When existing systems, designs, products, processes, or services are about to change regardless of reason.
•
When new applications are found the existing conditions of the systems, designs, products, processes, or service.
•
When improvements are considered for the existing systems, designs, products, processes, or services.
FMEA PROCEDURE 1. Describe the product/process and its function 2. Create a Block Diagram of the product or process 3. Complete the header on the FMEA Form worksheet 4. Use the diagram prepared above to begin listing items or functions 5. Identify Failure Modes 6. Each failure should be listed in technical 7. Describe the effects of those failure modes 8. Identify the causes for each failure mode 9. Enter the Probability factor 10. Identify Current Controls (design or process) 11. Determine the likelihood of Detection 12. Review Risk Priority Numbers (RPN). RPN = (Severity) x (Probability) x (Detection) 13. Determine Recommended Action(s) to address potential failures that have a high RPN 14. Assign Responsibility and a Target Completion Date for these actions
15. Indicate Actions Taken 16. Update the FMEA as the design or process changes, the assessment changes or new information becomes known.
FMEA Prerequisites Review Requiremen
Review FRACAS
Get System
Design Detail
Functional Block Diagram
Functional Block diagram
Determine Failure
Occurren ce
Severit
Functional Mode Analysis and preparation of worksheets
Detectio n
FMEA Work Sheet
Team Review
Team Review
Changes Propose Corrective Action
No changes required
required
Corrective Action
Distribute to s
Figure 1. FMEA Process
Design Engine
Technical
Reliable Equipment s
Manufacturin g
Benefits of FMEA FMEA is designed to assist the engineer improve the quality and reliability of design. Properly used the FMEA provides the engineer several benefits. Among others, these benefits include: •
Improve product/process reliability and quality
•
Increase customer satisfaction
•
Early identification and elimination of potential product/process failure modes
•
Prioritize product/process deficiencies
•
Capture engineering/organization knowledge
•
Emphasizes problem prevention
•
Documents risk and actions taken to reduce risk
•
Provide focus for improved testing and development
•
Minimizes late changes and associated cost
Catalyst for teamwork and idea exchange between functions Team for conducting/reviewing an FMEA – Project Manager – Design Engineer (hardware/software/systems) – Test Engineer – Reliability Engineer – Quality Engineer – Field Service Engineer – Manufacturing/Process Engineer – Safety Engineering Outside supplier engineering and/or manufacturing could be added to the team. Customer representation is recommended if a t development program between /supplier exists.
PURPOSE OF FMEA The purpose of performing an FMEA is to analyze the product's design characteristics relative to the planned manufacturing process and experiment design to ensure that the resultant product meets customer needs and expectations. When potential failure modes are identified, corrective action can be taken to eliminate them or to continually reduce a potential occurrence. The FMEA also documents the rationale for the chosen manufacturing process. It provides for an organized critical analysis of potential failure modes and the associated causes for the system being defined. The technique uses occurrence and detection probabilities in conjunction with severity criteria to develop a risk priority number (RPN) for ranking corrective action considerations.
FMEA's provide the engineer with a tool that can assist in providing reliable, safe, and customer pleasing products and processes. Since FMEA help the engineer identify potential product or process failures, they can use it to: •
Develop product or process requirements that minimize the likelihood of those failures.
•
Evaluate the requirements obtained from the customer or other participants in the design process to ensure that those requirements do not introduce potential failures.
•
Identify design characteristics that contribute to failures and design them out of the system or at least minimize the resulting effects.
•
Develop methods and procedures to develop and test the product/process to ensure that the failures have been successfully eliminated.
•
Track and manage potential risks in the design. Tracking the risks contributes to the development of corporate memory and the success of future products as well.
•
Ensure that any failures that could occur will not injure or seriously impact the customer of the product/process.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis [FMEA] Introduction Customers are placing increased demands on companies for high quality, reliable products. The increasing capabilities and functionality of many products are making it more difficult for manufacturers to maintain the quality and reliability. Traditionally, reliability has been achieved through extensive testing and use of techniques such as probabilistic reliability modeling. These are techniques done in the late stages of development. The challenge is to design in quality and reliability early in the development cycle. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is methodology for analyzing potential reliability problems early in the development cycle where it is easier to take actions to overcome these issues, thereby enhancing reliability through design. FMEA is used to identify potential failure modes, determine their effect on the operation of the product, and identify actions to mitigate the failures. A crucial step is anticipating what might go wrong with a product. While anticipating every failure mode is not possible, the development team should formulate as extensive a list of potential failure modes as possible. The early and consistent use of FMEAs in the design process allows the engineer to design out failures and produce reliable, safe, and customer pleasing products. FMEAs also capture historical information for use in future product improvement. TYPES OF FMEA'S There are several types of FMEAs, some are used much more often than others. FMEAs should always be done whenever failures would mean potential harm or injury to the of the end item being designed. The types of FMEA are: •
System - focuses on global system functions
•
Design - focuses on components and subsystems
•
Process - focuses on manufacturing and assembly processes
•
Service - focuses on service functions
•
Software - focuses on software functions
System FMEA This is used to analyze systems and subsystems in the early concept and design stage. A system FMEA focuses on potential failure modes between the functions of the system caused by system deficiencies. It includes the interactions between systems and elements of the system. The outputs of the system FMEA are •
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of system functions that could detect potential failure modes.
•
A potential list of design actions to eliminate failure modes, safety issues and reduces the occurrence.
The benefits of the system FEMA are that it: •
Helps to select the optimum system alternative.
•
Helps to determine redundancy.
•
Helps to define the basis for system level diagnostic procedures.
•
Increases the likelihood that potential problems will be considered.
•
Identifies potential system failures and their interaction with other systems.
Design FMEA This is used to analyze products before they are released to manufacturing. A design focuses on failure modes caused by design deficiencies. The outputs of the design FMEA are: -
•
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical and / or significant characteristics.
•
A potential list of design actions to eliminate failure modes, safety issues and reduces the occurrence.
•
A potential list of parameters for appropriate testing, inspection, and / or detection methods.
•
A potential list of recommended action for the critical and significant characteristics.
The benefits of design FMEA are that it: •
Establishes a priority for design improvement actions.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
•
Provides information to help through design verification and testing.
•
Helps to identify the critical or significant characteristics.
•
Assists in the evaluation of design requirements and alternatives.
•
Helps to identify and eliminate potential safety concerns.
•
Helps to identify product failure early in the product development phase.
Process FMEA This is used to analyze manufacturing and assembly processes. A process FMEA focuses on failure modes caused by process or assembly deficiencies. The outputs of the process FMEA are: •
A potential list of failure modes ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical and/ or significant characteristics.
•
A potential list of recommended actions to address the critical and significant characteristics.
•
A potential list to eliminate the causes of failure modes, reduce their occurrences, and improve defect detection if K cannot be improved.
The benefits of the process FMEA are that it: • Identifies process deficiencies and offers a corrective action plan. •
Identifies the critical and/ or significant characteristics and helps in developing control plans.
•
Establishes a priority of corrective actions.
•
Assists in the analysis of the manufacturing or assembly process.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
Service FMEA This is used to analyze services before they reach the customer. A service FMEA focuses on the failure modes (tasks, errors, mistakes) caused by system or process deficiencies. The outputs of the service FMEA are: •
A potential list of errors ranked by RPN.
•
A potential list of critical or significant tasks, or processes.
•
A potential list of bottleneck processes or tasks.
•
A potential list to eliminate the errors.
•
A potential list of monitoring system / process functions.
The benefits of the service FMEA are that it: •
Assists in the analysis of job flow.
•
Assists in the analysis of the system and/ or process.
•
Identifies task deficiencies.
•
Identifies critical or significant tasks and helps in the development of control plan.
•
Establishes a priority for improvement actions.
•
Documents the rationale for changes.
An FMEA program should start •
When new systems, designs, products, processes, or services are designed.
•
When existing systems, designs, products, processes, or services are about to change regardless of reason.
•
When new applications are found the existing conditions of the systems, designs, products, processes, or service.
•
When improvements are considered for the existing systems, designs, products, processes, or services.
FMEA PROCEDURE 1. Describe the product/process and its function 2. Create a Block Diagram of the product or process 3. Complete the header on the FMEA Form worksheet 4. Use the diagram prepared above to begin listing items or functions 5. Identify Failure Modes 6. Each failure should be listed in technical 7. Describe the effects of those failure modes 8. Identify the causes for each failure mode 9. Enter the Probability factor 10. Identify Current Controls (design or process) 11. Determine the likelihood of Detection 12. Review Risk Priority Numbers (RPN). RPN = (Severity) x (Probability) x (Detection) 13. Determine Recommended Action(s) to address potential failures that have a high RPN 14. Assign Responsibility and a Target Completion Date for these actions
15. Indicate Actions Taken 16. Update the FMEA as the design or process changes, the assessment changes or new information becomes known.