Bsbfia401 Ass4 1u3d48
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Bsbfia401 Ass4 as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 2,083
- Pages: 10
Assessment 4
1. For each of the following, state whether debit or credit increases the balance Answer: Asset
Debit
Expense
Debit
Liability
Credit
Equity
Credit
2 Which of the following is true? a) Credit entries in an asset decreases the balance b) Debit entries into a liability decreases the balance c) Debit entries into an equity increases the balance d) All of the Above Answe: All of the Above
3 What is the difference between single and double entry ing? Answer :The system of ing in which only one sided entry is required to record financial transactions is Single Entry System. The ing system, in which every transaction affects two s simultaneously is known as the Double Entry System
4 In double entry ing, which of the following examples would Total Assets remain unchanged? a) An s receivable is reclassified as revenue receivable b) An payable is paid to the creditor c) Depreciation expenses are recorded d) All of the above e) None of the above were inoperable 1
Answer : None of the above were inoperable
5 Describe AS/NZS 4360: 2004 Risk management.
6 Discuss and give an example of the following laws
Disability Legislation
Answer Disability is an impairment that may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, sensory, or some combination of these. It substaptially affects a person's life activities and may be present from birth or occur during a person's lifetime
Example Provision of goods, services and facilities. For example, when a person wants goods on services from shops, pubs and places of entertainment, cafes, video shops, banks, lawyers government departments, doctors, bospitals and so on
Industrial relations law
2
Answer :Industrial relatións is the management of work-related obligations and entitlements between employers and their employees
Example: A good example of this is the way in which pay rates and other conditions of work are negotiated between business owners and business employees. Business owners/managers have to take aćcount of minimum pay and conditions as prescribed in industrial relations regulations Industrial relations isn't just about pay and conditions, it is also about the manner in which all parties in the workplace i.e. business owners/managers and employees consult, negotiate and work together for common good.
Company Law
Answer Company law (or the law of business associations) is the sheld of law concerning companies and other business organizations
Example The largest companies are usually publicly sted on stock exchanges around the world Even single individuals, also known as sole traders may incorporate themselves and limit their liability in order to carry on a business. All différent forms of companies depend on the particular law of the particular country in which they reside
7 List 8 types of discrimination that are covered by your State Equal Opportunity Legislation Answer 1. race 2. colour 3. gender 4. sexual preference 5. religion 6. physical or mehtal disability 7. marital ştatus 8. family or carer's responsibilities 8 List 2 Commonwealth anti-discrimination Acts
3
Answer
1. Temporary exemptions The Australian Human Rights Commission is abfe to grant temporary exemptions from some parts of the Sex Discrimination Act, the Disability Discrimination Act and the Age Discrimination Act (section 44 SDA, section 55 DDA and section 44 ADA). The Racial Discrimination Act does not allow the granting of temporary exemptions. Thé Commission has developed criteria and procedures to determine when an exemption is appropriate. Under these criteria, any temporary exemption must be consistent with the objects ofthe Act. Temporary exemptions must be for a term of no more than five years, however, there is pfovision under the relevant Acts for the Commission to grant a further exemption on an applicatioń by the applicant. Public comment on exemption applications is generally sought beforethe Commission makes a decision. The Commission may also set conditions on temporary exemptions. Exemptions are commonly granted to allow time, where necessary, to make changes to comply with anti-discrimination legislation
2. Racial Discrimination Act There are no 'exemptions' under the Racial Discrimination Act. There are a statutory 'exceptions' to the operation of the Racial Discrimination Act
Section 8(1) - special measures' to which paragraph 4 of Article 1 of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination applies. Includes special measure purpose of securing advancement of certain racial or ethnic groups as may be necessary to ensure such groups equal enjoyment of human rights and fundamental freedoms (with certain provisos) .
Section 8(2)-instrument conferring charitable benefits to persons of a particular race, colour or national or ethnic origin
Sections 9(3) & 15(4) employment on a ship or aircraft if engaged outside Australia, and .
Sections 12(3) & 15(5)-accommodation and employment in private dwelling house or flat where the accommodation is shared with the person gr a relative of the person
4
9 Discuss the Federal Awards (Industrial Relations) Act 2003. What award conditions does this entitle workers to? Answer: "allowable award matters" has the same meaning as in the Commonwealth Act, as affected by item 50 of Schedule 5 to the Workplace Relations and Other Legislation Amendment Act 1996 of the Commonwealth "award" means award made under the Commonwealth Act
10 Discuss the Federal Workplace Relations Act 1996
Answer :The Workplace Relations Act 1996 was a law regarding workplace conditions and rights ed by the Howard Government after it came into power in 1996. It replaced the previous Labor Government's Industrial Relations Act 1988, and commenced operation on 1 January 1997
In 2005, the Workplace Relations Amendment Act 2005 was ed by the Howard Government. This amendment act came into effect on 27 March 2006 and substantially amended the original Act, bringing in the Work Choices changes to Austrálian labour law. The Act was repealed on 1 July 2009 by the Fair Work Act 2009 ed by the Rúdd Labor Government
11 Discuss possible repercussions, such as those under WHS legislation of an incident
involving an injury to an employee due to a negligent act by their employer
Answer :if you suffer significant injury and have been assessed as being a person who has sustained 15 % or greater whole person impairment you would be entitled to a future lump sum for wage loss additional to any payments you may have r parts of your body including arms legs eyes back neck and/or sexual performance.
It is important to note that once you receive a lump sum for wage loss your Workers Compensation comes to an end. Often from experience most people in such a situation are 5
happy to receive a lump sum payment so that they get on with the rest of their life-without continually dealing with insurance companies.
12 What is classified as Personal Information as per the National Privacy Principles Answer 1. Collection 2. Use and disclosure 3. Information quality 4. Information security 5. Openness 6. Access and correction 7. Identifiers 8. Anonymity 9. Transborder data flows 10. Sensitive information
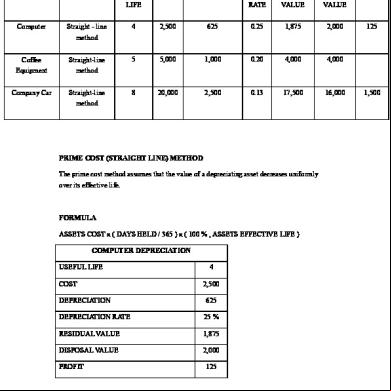
13 What is straight-line depreciation? Give an example
Answer :Straight line depreciation is the default method used to gradually reduce the carrying amount of a fixed asset over its useful life Example :Pensive calculates the annual straight-line depreciation for the machine of $60,000estimated salvage value of $10,000- Depreciable asset cost of $50,000. 1/ 5-year useful life 20 % depreciation rate per year . 20 % depreciation rate x $ 50,000 depreciable asset cost $10,000 annual depreciation.
14 What is the diminishing method of depreciation? Explain
Answer: Reducing balance depreciation (diminishing value) This method of depreciation involves multiplying the asset carrying amount by the depreciation rate to calculate the depreciation that can be claimed that year. 6
15 What types of tax liabilities are normally reported in the BAS Statement? Note do each item that is included in a BAS statement. The question is list the types of tax liabilities Answer 1. Goods and services tax (GST) 2. Pay as you go withholding tax 3. pay as you go instalment tax 4. Fringe benefit tax (FBT) 5. Luxury car tax (LCT) 6. Wine equalisation tax (WET) 7. Fuel tax credits
16 How often are businesses required to lodge BAS statements? Please explain your answer Answer :In Australia, the financial year for tax purposes runs from 1 July to 30 June. Businesses are required to lodge an income tax return for this period. If you operate your business as a sole trader you can declare your business income aş part of your personal income tax return.
17 Explain what an Instalment Notice for GST and PAYG instalments is. In your explanation indicate how an instalment notice differs from and activity statement Answer
GST instalments some used in our information about thegoods and services tax (GST) may be new to you or have a specific meaning in GST law.
PAYG instalments is a system for making regular payments towards your expected annual income tax liability. It only applies to you if you earn business and/or investment income over a certain amount.
GST 7
GST is a tax based on the transactions you make in your business-that is, the sales and purchases. There are some GST-free sales and purchases/like overseas sales and purchases, but in general the GST is 10 % of most of your business transactions . You need to your business for GST if you currently earn gross sales of $75,000 or móre in a financial year.
You can voluntarily your business for GST if you earn less than this amount. You may want to voluntarily if you are incurring a lot of expenses like when you are in startup mode. That way
Net GST payable Answer Consideration. This means the amount paid or payable for a good or service. It i money, but can include other goods and services or an act of forbearance. No GST is payable supply of a good or service if no consideration is made
20 Describe the process you should follow when reconciling a bank Answer : Bank Reconciliation process
1. Adjusting the Balance per Bank 2. Adjusting the Balance per Books 3. Comparing the Adjusted Balances 4. Preparing Journal Entries
21 What is accrual ing Answer :Accrual ing is an ing method that measures the performance and position of a company by recognizing economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur. The general idea is that economic events are recognized by matching revenues to expenses matching principle) at the time in which the transaction occurs rather than when payment (or received). This method allows the current cash inflows/outflows to be combined with future expected cash inflows/outflows to give a more accurate picture of a company's current financial condition.
8
22 Describe the following ing principles
Doctrine of Consistency answer :The consistency principle states that, once you adopt an ing principle or method, continue to follow it consistently in future ing periods. Only change an ing principle or method if the new version in some way improves reported financial results
Doctrine of Disclosure Answer :Inevitable disclosure is a legal doctrine through which an employer can claim trade secret en a former employee from working in a job that may result in the use of trade secrets without the need for proof or evidence.
Doctrine of Materiality
Answer The materiality principle states that an ing standard can be ignored if the net imp of doing so has such a small impact on the financial statements that a reader of the financial statements would not be misled
Doctrine of Conservatism
Answer :The convention of conservatism, also known as the doctrine of prudence in ing is a policy of anticipating possible future losses but not future gains. This policy tends to understate rather than overstate net assets and net income, and therefore lead companies to "play safe".
23 What is the objective of ing Standard AAS 3?
Answer The Financial ing Standards Boards Statements of Financial ing Concepts No. 1 states the objective of business financial reporting, which is to provide 9
information that is useful for making business and economic decisions. Specifically, the information should be useful t investors and lenders, be helpful in determining a company's cash flows, and report the company's assets, liabilities, and owner's equity and the changes in them.
With these objectives in mind, financial ants produce financial statements based on the ing standards in a given jurisdiction. These standards may be the generally accepted ing principles of a respective country, which are typically issued by a national stand setter, or International Financial Reporting Standards which are issued by the International ing Standards Board.
10
1. For each of the following, state whether debit or credit increases the balance Answer: Asset
Debit
Expense
Debit
Liability
Credit
Equity
Credit
2 Which of the following is true? a) Credit entries in an asset decreases the balance b) Debit entries into a liability decreases the balance c) Debit entries into an equity increases the balance d) All of the Above Answe: All of the Above
3 What is the difference between single and double entry ing? Answer :The system of ing in which only one sided entry is required to record financial transactions is Single Entry System. The ing system, in which every transaction affects two s simultaneously is known as the Double Entry System
4 In double entry ing, which of the following examples would Total Assets remain unchanged? a) An s receivable is reclassified as revenue receivable b) An payable is paid to the creditor c) Depreciation expenses are recorded d) All of the above e) None of the above were inoperable 1
Answer : None of the above were inoperable
5 Describe AS/NZS 4360: 2004 Risk management.
6 Discuss and give an example of the following laws
Disability Legislation
Answer Disability is an impairment that may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, sensory, or some combination of these. It substaptially affects a person's life activities and may be present from birth or occur during a person's lifetime
Example Provision of goods, services and facilities. For example, when a person wants goods on services from shops, pubs and places of entertainment, cafes, video shops, banks, lawyers government departments, doctors, bospitals and so on
Industrial relations law
2
Answer :Industrial relatións is the management of work-related obligations and entitlements between employers and their employees
Example: A good example of this is the way in which pay rates and other conditions of work are negotiated between business owners and business employees. Business owners/managers have to take aćcount of minimum pay and conditions as prescribed in industrial relations regulations Industrial relations isn't just about pay and conditions, it is also about the manner in which all parties in the workplace i.e. business owners/managers and employees consult, negotiate and work together for common good.
Company Law
Answer Company law (or the law of business associations) is the sheld of law concerning companies and other business organizations
Example The largest companies are usually publicly sted on stock exchanges around the world Even single individuals, also known as sole traders may incorporate themselves and limit their liability in order to carry on a business. All différent forms of companies depend on the particular law of the particular country in which they reside
7 List 8 types of discrimination that are covered by your State Equal Opportunity Legislation Answer 1. race 2. colour 3. gender 4. sexual preference 5. religion 6. physical or mehtal disability 7. marital ştatus 8. family or carer's responsibilities 8 List 2 Commonwealth anti-discrimination Acts
3
Answer
1. Temporary exemptions The Australian Human Rights Commission is abfe to grant temporary exemptions from some parts of the Sex Discrimination Act, the Disability Discrimination Act and the Age Discrimination Act (section 44 SDA, section 55 DDA and section 44 ADA). The Racial Discrimination Act does not allow the granting of temporary exemptions. Thé Commission has developed criteria and procedures to determine when an exemption is appropriate. Under these criteria, any temporary exemption must be consistent with the objects ofthe Act. Temporary exemptions must be for a term of no more than five years, however, there is pfovision under the relevant Acts for the Commission to grant a further exemption on an applicatioń by the applicant. Public comment on exemption applications is generally sought beforethe Commission makes a decision. The Commission may also set conditions on temporary exemptions. Exemptions are commonly granted to allow time, where necessary, to make changes to comply with anti-discrimination legislation
2. Racial Discrimination Act There are no 'exemptions' under the Racial Discrimination Act. There are a statutory 'exceptions' to the operation of the Racial Discrimination Act
Section 8(1) - special measures' to which paragraph 4 of Article 1 of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination applies. Includes special measure purpose of securing advancement of certain racial or ethnic groups as may be necessary to ensure such groups equal enjoyment of human rights and fundamental freedoms (with certain provisos) .
Section 8(2)-instrument conferring charitable benefits to persons of a particular race, colour or national or ethnic origin
Sections 9(3) & 15(4) employment on a ship or aircraft if engaged outside Australia, and .
Sections 12(3) & 15(5)-accommodation and employment in private dwelling house or flat where the accommodation is shared with the person gr a relative of the person
4
9 Discuss the Federal Awards (Industrial Relations) Act 2003. What award conditions does this entitle workers to? Answer: "allowable award matters" has the same meaning as in the Commonwealth Act, as affected by item 50 of Schedule 5 to the Workplace Relations and Other Legislation Amendment Act 1996 of the Commonwealth "award" means award made under the Commonwealth Act
10 Discuss the Federal Workplace Relations Act 1996
Answer :The Workplace Relations Act 1996 was a law regarding workplace conditions and rights ed by the Howard Government after it came into power in 1996. It replaced the previous Labor Government's Industrial Relations Act 1988, and commenced operation on 1 January 1997
In 2005, the Workplace Relations Amendment Act 2005 was ed by the Howard Government. This amendment act came into effect on 27 March 2006 and substantially amended the original Act, bringing in the Work Choices changes to Austrálian labour law. The Act was repealed on 1 July 2009 by the Fair Work Act 2009 ed by the Rúdd Labor Government
11 Discuss possible repercussions, such as those under WHS legislation of an incident
involving an injury to an employee due to a negligent act by their employer
Answer :if you suffer significant injury and have been assessed as being a person who has sustained 15 % or greater whole person impairment you would be entitled to a future lump sum for wage loss additional to any payments you may have r parts of your body including arms legs eyes back neck and/or sexual performance.
It is important to note that once you receive a lump sum for wage loss your Workers Compensation comes to an end. Often from experience most people in such a situation are 5
happy to receive a lump sum payment so that they get on with the rest of their life-without continually dealing with insurance companies.
12 What is classified as Personal Information as per the National Privacy Principles Answer 1. Collection 2. Use and disclosure 3. Information quality 4. Information security 5. Openness 6. Access and correction 7. Identifiers 8. Anonymity 9. Transborder data flows 10. Sensitive information
13 What is straight-line depreciation? Give an example
Answer :Straight line depreciation is the default method used to gradually reduce the carrying amount of a fixed asset over its useful life Example :Pensive calculates the annual straight-line depreciation for the machine of $60,000estimated salvage value of $10,000- Depreciable asset cost of $50,000. 1/ 5-year useful life 20 % depreciation rate per year . 20 % depreciation rate x $ 50,000 depreciable asset cost $10,000 annual depreciation.
14 What is the diminishing method of depreciation? Explain
Answer: Reducing balance depreciation (diminishing value) This method of depreciation involves multiplying the asset carrying amount by the depreciation rate to calculate the depreciation that can be claimed that year. 6
15 What types of tax liabilities are normally reported in the BAS Statement? Note do each item that is included in a BAS statement. The question is list the types of tax liabilities Answer 1. Goods and services tax (GST) 2. Pay as you go withholding tax 3. pay as you go instalment tax 4. Fringe benefit tax (FBT) 5. Luxury car tax (LCT) 6. Wine equalisation tax (WET) 7. Fuel tax credits
16 How often are businesses required to lodge BAS statements? Please explain your answer Answer :In Australia, the financial year for tax purposes runs from 1 July to 30 June. Businesses are required to lodge an income tax return for this period. If you operate your business as a sole trader you can declare your business income aş part of your personal income tax return.
17 Explain what an Instalment Notice for GST and PAYG instalments is. In your explanation indicate how an instalment notice differs from and activity statement Answer
GST instalments some used in our information about thegoods and services tax (GST) may be new to you or have a specific meaning in GST law.
PAYG instalments is a system for making regular payments towards your expected annual income tax liability. It only applies to you if you earn business and/or investment income over a certain amount.
GST 7
GST is a tax based on the transactions you make in your business-that is, the sales and purchases. There are some GST-free sales and purchases/like overseas sales and purchases, but in general the GST is 10 % of most of your business transactions . You need to your business for GST if you currently earn gross sales of $75,000 or móre in a financial year.
You can voluntarily your business for GST if you earn less than this amount. You may want to voluntarily if you are incurring a lot of expenses like when you are in startup mode. That way
Net GST payable Answer Consideration. This means the amount paid or payable for a good or service. It i money, but can include other goods and services or an act of forbearance. No GST is payable supply of a good or service if no consideration is made
20 Describe the process you should follow when reconciling a bank Answer : Bank Reconciliation process
1. Adjusting the Balance per Bank 2. Adjusting the Balance per Books 3. Comparing the Adjusted Balances 4. Preparing Journal Entries
21 What is accrual ing Answer :Accrual ing is an ing method that measures the performance and position of a company by recognizing economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur. The general idea is that economic events are recognized by matching revenues to expenses matching principle) at the time in which the transaction occurs rather than when payment (or received). This method allows the current cash inflows/outflows to be combined with future expected cash inflows/outflows to give a more accurate picture of a company's current financial condition.
8
22 Describe the following ing principles
Doctrine of Consistency answer :The consistency principle states that, once you adopt an ing principle or method, continue to follow it consistently in future ing periods. Only change an ing principle or method if the new version in some way improves reported financial results
Doctrine of Disclosure Answer :Inevitable disclosure is a legal doctrine through which an employer can claim trade secret en a former employee from working in a job that may result in the use of trade secrets without the need for proof or evidence.
Doctrine of Materiality
Answer The materiality principle states that an ing standard can be ignored if the net imp of doing so has such a small impact on the financial statements that a reader of the financial statements would not be misled
Doctrine of Conservatism
Answer :The convention of conservatism, also known as the doctrine of prudence in ing is a policy of anticipating possible future losses but not future gains. This policy tends to understate rather than overstate net assets and net income, and therefore lead companies to "play safe".
23 What is the objective of ing Standard AAS 3?
Answer The Financial ing Standards Boards Statements of Financial ing Concepts No. 1 states the objective of business financial reporting, which is to provide 9
information that is useful for making business and economic decisions. Specifically, the information should be useful t investors and lenders, be helpful in determining a company's cash flows, and report the company's assets, liabilities, and owner's equity and the changes in them.
With these objectives in mind, financial ants produce financial statements based on the ing standards in a given jurisdiction. These standards may be the generally accepted ing principles of a respective country, which are typically issued by a national stand setter, or International Financial Reporting Standards which are issued by the International ing Standards Board.
10