Difference Between Windows Server 2003 And 2008 And 2012 1x2130
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Difference Between Windows Server 2003 And 2008 And 2012 as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 2,616
- Pages: 11
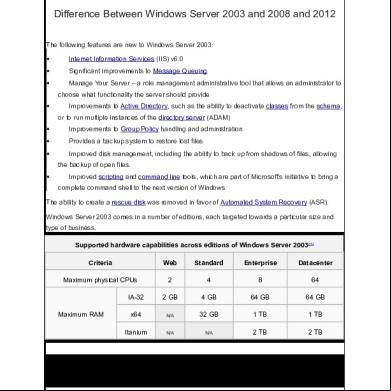
Difference Between Windows Server 2003 and 2008 and 2012 The following features are new to Windows Server 2003:
Internet Information Services (IIS) v6.0
Significant improvements to Message Queuing
Manage Your Server – a role management istrative tool that allows an to choose what functionality the server should provide
Improvements to Active Directory, such as the ability to deactivate classes from the schema, or to run multiple instances of the directory server (ADAM)
Improvements to Group Policy handling and istration
Provides a backup system to restore lost files
Improved disk management, including the ability to back up from shadows of files, allowing the backup of open files.
Improved scripting and command line tools, which are part of Microsoft's initiative to bring a complete command shell to the next version of Windows
The ability to create a rescue disk was removed in favor of Automated System Recovery (ASR). Windows Server 2003 comes in a number of editions, each targeted towards a particular size and type of business. ed hardware capabilities across editions of Windows Server 2003 [15] Criteria
Web
Standard
Enterprise
Datacenter
Maximum physical Us
2
4
8
64
IA-32
2 GB
4 GB
64 GB
64 GB
x64
N/A
32 GB
1 TB
1 TB
Itanium
N/A
N/A
2 TB
2 TB
Maximum RAM
Windows Server 2008 Features Windows Server 2008 is built from the same code base as Windows Vista; therefore, it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the code base is common, it automatically comes with most of the technical, security, management and istrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and ASLR (address space layout randomization); improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices, to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using Dynamic Hardware Partitioning; each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.
Server Core
Default interface for Server Core. Because Windows Explorer is removed from Server Core, programs such as Notepad use theWindows NT 3.x-style file dialog.
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console. However, Notepad and some control applets, such as Regional Settings, are available. Server Core does not include the .NET Framework, Internet Explorer, Windows PowerShell or many other features not related to core server features. A Server Core machine can be configured for several basic roles: Domain controller/Active Directory Domain Services, ADLDS (ADAM), DNS Server, DH server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, IIS 7 web server and HyperV virtual server. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core
Active Directory roles Active Directory roles are expanded with identity, certificate, and rights management services. Active Directory, until Windows Server 2003, allowed network s to centrally manage connected computers, to set policies for groups of s, and to centrally deploy new applications to multiple computers. This role of Active Directory is being renamed as Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS). A number of other additional services are being introduced, including Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM), Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS), and Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS). Identity and certificate services allow s to manage s and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Federation management services enable enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use his company name and to on a client's network. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services. Each of these services represents a server role.
Failover Clustering Windows Server 2008 offers high-availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime. In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. With the cluster validation wizard, an can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be ed on a given configuration. Note: This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V architecture
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft's virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system's kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized. A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft's release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 20znCFnzd. Also, a standalone version of Hyper-V exists; this version s only x86-64 architecture.While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources aprocess or a can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. U time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008. It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard SCW from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations s would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role. [18]
System requirements System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows: Criteria
2008
2008 R2
Minimum
Recommended
1 GHz (IA-32)
U
1.4 GHz (x86-
Minimum 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or
2 GHz
512 MB
2 GHz
Itanium)
64 or Itanium) RAM
Recommended
2 GB
512 MB
2 GB
Other editions,
32-bit: 20 GB HDD[a]
Other editions,
Foundation:
10 GB
40 GB
64-bit: 32 GB
Foundation:
10 GB
Other
Other
editions: 32 GB
Foundation: 10
editions: 32 GB
GB[39] Device
DVD drive, 800 × 600 display, keyboard and mouse
s
Scalability Windows Server 2008 s the following maximum hardware specifications: Specification Physical processors ("sockets")
Windows Server 2008 SP2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Standard: 4
Standard: 4
Enterprise: 8
Enterprise: 8
Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled
Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled
IA-32: 32
Datacenter: 64 256
x64: 64 IA-32: N/A
Memory
Datacenter: 32
64
x64: 24 Standard, Web: 4 GB Enterprise, Datacenter: 64
on IA-32
N/A
GB
Memory on x64
Standard, Web: 32 GB HPC: 128 GB
Foundation: 8 GB
Enterprise, Datacenter: 1
Standard, Web: 32 GB
HPC: 128 GB
TB Memory
Enterprise, Datacenter:
2 TB
on Itanium
2 TB 2 TB
Windows Server 2012 Features Installation options Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 can switch between "Server Core" and "Server with a GUI" installation options without a full reinstallation. Server Core - an option with a command-line interface only - is now the recommended configuration. There is also a third installation option that allows some GUI elements such as MMC and Server Manager to run, but without the normal desktop, shell or default programs like File Explorer
interface Server Manager has been redesigned with an emphasis on easing management of multiple servers. The operating system, like Windows 8, uses the Metro-based interface unless installed in Server Core mode. Windows Store is available in this version of Windows but is not installed by default. Windows PowerShell in this version has over 2300 commandlets, compared to around 200 in Windows Server 2008 R2
Task Manager Windows Server 2012 includes a new version of Windows Task Manager together with the old version. In the new version the tabs are hidden by default, showing applications only. In the new Processes tab, the processes are displayed in varying shades of yellow, with darker shades representing heavier resource use. It lists application names and status, as well as U, memory, hard disk and network utilization. The process information found in the older versions are now moved to the new Details tab. The Performance tab shows "U", "Memory", "Disk", "Wi-Fi" and "Ethernet" graphs. The U tab no longer displays individual graphs for every logical processor on the system by default, although that remains an option. Additionally, it can display data for each non-uniform memory access (NUMA) node. When displaying data for each logical processor for machines with more than 64 logical processors, the U tab now displays simple utilization percentages on heat-mapping tiles.The color used for these heat maps is blue, with
darker shades again indicating heavier utilization. Hovering the cursor over any logical processor's data now shows the NUMA node of that processor and its ID, if applicable. Additionally, a new Startup tab has been added that lists startup applications, however this tab does not exist in Windows Server 2012.The new task manager recognizes when a Windows Store app has the "Suspended" status.
IP address management (IPAM) Windows Server 2012 has an IP address management role for discovering, monitoring, auditing, and managing the IP address space used on a corporate network. The IPAM is used for the management and monitoring of Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DH) servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 are fully ed.
Active Directory Windows Server 2012 has a number of changes to Active Directory from the version shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2. The Active Directory Domain Services installation wizard has been replaced by a new section in Server Manager, and a GUI has been added to the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Multiple policies can be set in the same domain. Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 is now aware of any changes resulting from virtualization, and virtualized domain controllers can be safely cloned. Upgrades of the domain functional level to Windows Server 2012 are simplified; it can be performed entirely in Server Manager. Active Directory Federation Services is no longer required to be ed when installed as a role, and claims which can be used by the Active Directory Federation Services have been introduced into the Kerberos token. Windows Powershell commands used by Active Directory istrative Center can be viewed in a "Powershell History Viewer”.
Hyper-V Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V, as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event. Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premises connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format). Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster. SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role.
ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS), codenamed "Protogon" is a new file system in Windows Server 2012 initially intended for file servers that improves on NTFS in some respects. Major new features of ReFS include: Some NTFS features are not ed in ReFS, including named streams, object IDs, short names, file compression, file level encryption (EFS), data transactions, hard links, extended attributes, and disk quotas, Sparse files are
IIS 8.0 Specifications
Foundation[55]
Essentials
Distribution
OEM only
Retail, volume licensing, OEM
Licensing model
Per server
Per server
1
2
32 GB
64 GB
15
25
1 standalone DFS root
1 standalone DFS root
Processor chip limi
Memory limit
limit
File sharing limits
Network Policy and Access Services limits
Remote Desktop Services limits
Virtualization rights
50 RRAS connections and 10 IAS connections
50 Remote Desktop Services connections
N/A
250 RRAS connections, 50 IAS connec 2 IAS Server Groups
Gateway only
Either in 1 VM or 1 physical server, but n
once
Active Directory Lightweight
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Application server role
Yes
Partial
DH role
Yes
Yes
DNS server role
Yes
Yes
Fax server role
Yes
Yes
Print and document services
Yes
Yes
Server Manager
Yes
Yes
UDDI services
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Directory Services
Active Directory Federation Services
Active Directory Rights Management Services
Web services (Internet Information Services)
Windows Deployment Services
Yes
Yes
Windows Powershell
Yes
Yes
Must be root of forest and domain
Yes
Certificate Authorities only
Certificate Authorities only
Hyper-V
No
No
Server Core mode
No
No
Windows Server Update Services
No
No
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Certificate Services
Windows Server 2012 includes version 8.0 of Internet Information Services (IIS).
Scalability Windows Server 2012 s the following maximum hardware specifications, Windows Server 2012 improves over its predecessor Windows Server 2008 R2: Specification
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2008 R2
Physical processors
64
64
640
256
320
64
4 TB
2 TB
64
16
Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled Memory Failover cluster nodes (in any single cluster)
System requirements Minimum system requirements for Windows Server 2012 Processor
1.4 GHz, x64
Memory
512 MB
Free disk space
32 GB (more if there is at least 16 GB of RAM)
Windows Server 2012 runs only on x64 processors. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 does not Itanium. Upgrades from Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 are ed, although upgrades from prior releases are not.
Editions Windows Server 2012 has four editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard and Datacenter.
Internet Information Services (IIS) v6.0
Significant improvements to Message Queuing
Manage Your Server – a role management istrative tool that allows an to choose what functionality the server should provide
Improvements to Active Directory, such as the ability to deactivate classes from the schema, or to run multiple instances of the directory server (ADAM)
Improvements to Group Policy handling and istration
Provides a backup system to restore lost files
Improved disk management, including the ability to back up from shadows of files, allowing the backup of open files.
Improved scripting and command line tools, which are part of Microsoft's initiative to bring a complete command shell to the next version of Windows
The ability to create a rescue disk was removed in favor of Automated System Recovery (ASR). Windows Server 2003 comes in a number of editions, each targeted towards a particular size and type of business. ed hardware capabilities across editions of Windows Server 2003 [15] Criteria
Web
Standard
Enterprise
Datacenter
Maximum physical Us
2
4
8
64
IA-32
2 GB
4 GB
64 GB
64 GB
x64
N/A
32 GB
1 TB
1 TB
Itanium
N/A
N/A
2 TB
2 TB
Maximum RAM
Windows Server 2008 Features Windows Server 2008 is built from the same code base as Windows Vista; therefore, it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the code base is common, it automatically comes with most of the technical, security, management and istrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and ASLR (address space layout randomization); improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices, to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using Dynamic Hardware Partitioning; each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.
Server Core
Default interface for Server Core. Because Windows Explorer is removed from Server Core, programs such as Notepad use theWindows NT 3.x-style file dialog.
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console. However, Notepad and some control applets, such as Regional Settings, are available. Server Core does not include the .NET Framework, Internet Explorer, Windows PowerShell or many other features not related to core server features. A Server Core machine can be configured for several basic roles: Domain controller/Active Directory Domain Services, ADLDS (ADAM), DNS Server, DH server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, IIS 7 web server and HyperV virtual server. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core
Active Directory roles Active Directory roles are expanded with identity, certificate, and rights management services. Active Directory, until Windows Server 2003, allowed network s to centrally manage connected computers, to set policies for groups of s, and to centrally deploy new applications to multiple computers. This role of Active Directory is being renamed as Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS). A number of other additional services are being introduced, including Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM), Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS), and Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS). Identity and certificate services allow s to manage s and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Federation management services enable enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use his company name and to on a client's network. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services. Each of these services represents a server role.
Failover Clustering Windows Server 2008 offers high-availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime. In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. With the cluster validation wizard, an can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be ed on a given configuration. Note: This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V architecture
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft's virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system's kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized. A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft's release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 20znCFnzd. Also, a standalone version of Hyper-V exists; this version s only x86-64 architecture.While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources aprocess or a can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. U time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008. It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard SCW from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations s would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role. [18]
System requirements System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows: Criteria
2008
2008 R2
Minimum
Recommended
1 GHz (IA-32)
U
1.4 GHz (x86-
Minimum 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or
2 GHz
512 MB
2 GHz
Itanium)
64 or Itanium) RAM
Recommended
2 GB
512 MB
2 GB
Other editions,
32-bit: 20 GB HDD[a]
Other editions,
Foundation:
10 GB
40 GB
64-bit: 32 GB
Foundation:
10 GB
Other
Other
editions: 32 GB
Foundation: 10
editions: 32 GB
GB[39] Device
DVD drive, 800 × 600 display, keyboard and mouse
s
Scalability Windows Server 2008 s the following maximum hardware specifications: Specification Physical processors ("sockets")
Windows Server 2008 SP2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Standard: 4
Standard: 4
Enterprise: 8
Enterprise: 8
Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled
Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled
IA-32: 32
Datacenter: 64 256
x64: 64 IA-32: N/A
Memory
Datacenter: 32
64
x64: 24 Standard, Web: 4 GB Enterprise, Datacenter: 64
on IA-32
N/A
GB
Memory on x64
Standard, Web: 32 GB HPC: 128 GB
Foundation: 8 GB
Enterprise, Datacenter: 1
Standard, Web: 32 GB
HPC: 128 GB
TB Memory
Enterprise, Datacenter:
2 TB
on Itanium
2 TB 2 TB
Windows Server 2012 Features Installation options Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 can switch between "Server Core" and "Server with a GUI" installation options without a full reinstallation. Server Core - an option with a command-line interface only - is now the recommended configuration. There is also a third installation option that allows some GUI elements such as MMC and Server Manager to run, but without the normal desktop, shell or default programs like File Explorer
interface Server Manager has been redesigned with an emphasis on easing management of multiple servers. The operating system, like Windows 8, uses the Metro-based interface unless installed in Server Core mode. Windows Store is available in this version of Windows but is not installed by default. Windows PowerShell in this version has over 2300 commandlets, compared to around 200 in Windows Server 2008 R2
Task Manager Windows Server 2012 includes a new version of Windows Task Manager together with the old version. In the new version the tabs are hidden by default, showing applications only. In the new Processes tab, the processes are displayed in varying shades of yellow, with darker shades representing heavier resource use. It lists application names and status, as well as U, memory, hard disk and network utilization. The process information found in the older versions are now moved to the new Details tab. The Performance tab shows "U", "Memory", "Disk", "Wi-Fi" and "Ethernet" graphs. The U tab no longer displays individual graphs for every logical processor on the system by default, although that remains an option. Additionally, it can display data for each non-uniform memory access (NUMA) node. When displaying data for each logical processor for machines with more than 64 logical processors, the U tab now displays simple utilization percentages on heat-mapping tiles.The color used for these heat maps is blue, with
darker shades again indicating heavier utilization. Hovering the cursor over any logical processor's data now shows the NUMA node of that processor and its ID, if applicable. Additionally, a new Startup tab has been added that lists startup applications, however this tab does not exist in Windows Server 2012.The new task manager recognizes when a Windows Store app has the "Suspended" status.
IP address management (IPAM) Windows Server 2012 has an IP address management role for discovering, monitoring, auditing, and managing the IP address space used on a corporate network. The IPAM is used for the management and monitoring of Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DH) servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 are fully ed.
Active Directory Windows Server 2012 has a number of changes to Active Directory from the version shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2. The Active Directory Domain Services installation wizard has been replaced by a new section in Server Manager, and a GUI has been added to the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Multiple policies can be set in the same domain. Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 is now aware of any changes resulting from virtualization, and virtualized domain controllers can be safely cloned. Upgrades of the domain functional level to Windows Server 2012 are simplified; it can be performed entirely in Server Manager. Active Directory Federation Services is no longer required to be ed when installed as a role, and claims which can be used by the Active Directory Federation Services have been introduced into the Kerberos token. Windows Powershell commands used by Active Directory istrative Center can be viewed in a "Powershell History Viewer”.
Hyper-V Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V, as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event. Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premises connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format). Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster. SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role.
ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS), codenamed "Protogon" is a new file system in Windows Server 2012 initially intended for file servers that improves on NTFS in some respects. Major new features of ReFS include: Some NTFS features are not ed in ReFS, including named streams, object IDs, short names, file compression, file level encryption (EFS), data transactions, hard links, extended attributes, and disk quotas, Sparse files are
IIS 8.0 Specifications
Foundation[55]
Essentials
Distribution
OEM only
Retail, volume licensing, OEM
Licensing model
Per server
Per server
1
2
32 GB
64 GB
15
25
1 standalone DFS root
1 standalone DFS root
Processor chip limi
Memory limit
limit
File sharing limits
Network Policy and Access Services limits
Remote Desktop Services limits
Virtualization rights
50 RRAS connections and 10 IAS connections
50 Remote Desktop Services connections
N/A
250 RRAS connections, 50 IAS connec 2 IAS Server Groups
Gateway only
Either in 1 VM or 1 physical server, but n
once
Active Directory Lightweight
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Application server role
Yes
Partial
DH role
Yes
Yes
DNS server role
Yes
Yes
Fax server role
Yes
Yes
Print and document services
Yes
Yes
Server Manager
Yes
Yes
UDDI services
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Directory Services
Active Directory Federation Services
Active Directory Rights Management Services
Web services (Internet Information Services)
Windows Deployment Services
Yes
Yes
Windows Powershell
Yes
Yes
Must be root of forest and domain
Yes
Certificate Authorities only
Certificate Authorities only
Hyper-V
No
No
Server Core mode
No
No
Windows Server Update Services
No
No
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Certificate Services
Windows Server 2012 includes version 8.0 of Internet Information Services (IIS).
Scalability Windows Server 2012 s the following maximum hardware specifications, Windows Server 2012 improves over its predecessor Windows Server 2008 R2: Specification
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2008 R2
Physical processors
64
64
640
256
320
64
4 TB
2 TB
64
16
Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled Memory Failover cluster nodes (in any single cluster)
System requirements Minimum system requirements for Windows Server 2012 Processor
1.4 GHz, x64
Memory
512 MB
Free disk space
32 GB (more if there is at least 16 GB of RAM)
Windows Server 2012 runs only on x64 processors. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 does not Itanium. Upgrades from Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 are ed, although upgrades from prior releases are not.
Editions Windows Server 2012 has four editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard and Datacenter.