Examination Of An Ulcer 3m1n4w
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Examination Of An Ulcer as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 1,553
- Pages: 65
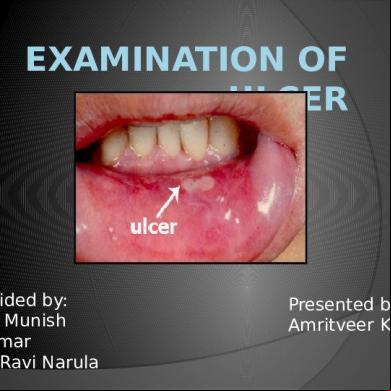
EXAMINATION OF ULCER
Guided by: Dr. Munish Kumar Dr.Ravi Narula
Presented by: Amritveer Kaur
An ulcer is the break in the continuity of covering epithelium-skin or mucous membrane
Follow the molecular death of the covering epithelium or its traumatic removal
S .DAS
PARTS OF ULCER
Margin Edge Floor Base
S .DAS
CLASSIFICATION OF ULCERS • TWO TYPES OF CLASSIFICATON OF ULCERS IS POSSIBLE:1.
CLINICAL:
2.
PATHOLOGICAL
S .DAS
Callous/ Chronic
S .DAS
Arterial, Traumatic,
S .DAS
HISTORY
Mode of onset Duration Pain Discharge Associated disease
S .DAS
1) Mode of onset
How ulcer developed ??
Traumatic- Eg.dental ulcer of the tongue
Spontaneously- may develop following a swelling which may be matted tuberculous lymph node or gumma or a rapidly growing malignant tumour ( malignant melanoma)
S .DAS
Marjolins ulcer- on burn scar
S .DAS
2) DURATION
How long??
Acute ulcer,chronic ulcer
Incubation period-time interval between exposure and the onset
S .DAS
3) PAIN
IsInflammatory the ulcer painful?? ulcers
S .DAS
4) DISCHARGE
Does the ulcer discharge or not??
Nature of discharge-serum, pus or blood
S .DAS
5) ASSOCIATED DISEASE
Nervous diseases Tuberculosis Diabetes syphillis
S .DAS
LOCAL EXAMINATION
Inspection Palpation Lymph Nodes
S .DAS
A ) Inspection
Size & Shape Number Position Edge, Margin, Floor Discharge Surrounding area
S .DAS
1. Size & Shape Tuberculous
S .DAS
2. Number
Tuberculous ,gummatous,varicose ulcers and soft chancres may be more than one in number
S .DAS
3. Position RODENT ULCERS
S .DAS
Anywhere Over Where subcutaneous in the bones such as
S .DAS
4.EDGE
Area between the margin and the floor
An ulcer has a margin or edge which takes characteristic shape in a particular form of ulcer
Gives clue to the diagnosis of ulcer also to the condition of ulcer
S .DAS
TYPES OF EDGES
Undermined edges Punched out edges Sloping Raised and pearly white beaded Everted
S .DAS
UNDERMINED EDGES
Mostly seen in tuberculosis Subcutaneous tissue destroyed faster than skin Overlying skin is thin friable ,reddish blue and unhealthy
S .DAS
Undermining of edges
S .DAS
PUNCHED OUT EDGE
Gummatus ulcer or in deep trophic ulcer Edge drops down at right angles to skin surface Disease which causes the ulcer itself do not tend to spread to the surrounding tissue
S .DAS
Punched out ulcers as seen in vasculitis
S .DAS
SLOPING EDGE
Healing traumatic or venous ulcers Reddish purple in color Consists of new healthy epithelium
S .DAS
Healing traumatic ulcer
S .DAS
RAISED AND PEARLY WHITE BEADED EDGE
Rodent ulcer Develops in invasive cellular disease and becomes necrotic at centre
S .DAS
BCC WITH TYPICAL ROLLED PEARLY WHITE EDGES
S .DAS
ROLLED OUT EVERTED EDGE Squamous cell carcinoma or an ulcerated adenocarcinoma Caused by fast growing cellular disease , growing portion at the edge of ulcer heaps up and spills over normal skin to produce an everted edge
S .DAS
SCC BUCCAL MUCOSA
S .DAS
Healing ulcer- blue zone (growing spreading ulcer- edge is inflammed and oedematous epi) and a white zone (fibrosis) S .DAS
5.FLOOR
Exposed surface of the ulcer
When floor is covered with red granulation tissue ulcer seems to be healthy and healing
Pale and smooth granulation tissue-slowely healing ulcer
Wash leather slough-gummatous ulcer S .DAS
Trophic ulcer penetrates down even to the bone-which forms the floor in that case
A black mass at the floor suggests malignat melanoma
S .DAS
A black mass at floor suggests malignant melanoma S .DAS
6.Discharge
Character
Its amount and smell
Healing ulcer-scanty serous discharge
Spreading and inflammed ulcer-purulent discharge
Malignant ulcer-sero-sanguineous discharge S .DAS
7. Surrounding area
glossy ,red and oedematous Acutely inflammed-
Scar or wrinkling – old case of tuberculosis
Dark pigmentation & eczema → varicose ulcer
Hypopigmentation → non-healing ulcer
S .DAS
B. PALPATION
Tenderness Edge and margin Base Depth Bleeding Relations to deeper structures Surrounding skin
S .DAS
1. Tenderness Acutely
S .DAS
2. Edge and margin
Marked Induration-squamous cell carcinoma
Slight induration- chronic ulcer
S .DAS
3. Base
On which the ulcer rests Better felt than seen
If an attempt is made to lift the ulcer between the thumb and index finger, base will be felt
Slight induration at the base-chronic ulcer Marked induration (hardness)-squamous cell carcinoma
S .DAS
Relations to deeper structures
Gummatous ulcer over subcutaneous bone (tibia,sternum) –often fixed Malignant also fixed
S .DAS
Surrounding skin
temperature & tenderness Mobility Fixity to deeper structure –malignant lesion For nerve lesion
S .DAS
C.EXAMINATION OF LYMPH NODES
Acute ulcers –regional lymph nodes enlarged tender
Tuberculous ulcers-enlarged ,matted ,slightly tender
Malignant ulcers-stony hard and fixed
S .DAS
SPECIAL INVESTIGATIONS
Routine blood examination Bacteriological examination of the discharge Chest X-Ray Biopsy
S .DAS
ORAL ULCERS
Erosion / Ulcer
Erosion –shallow crater in the epithelial surface , erythematous area, implies only superficial damage
Ulcer –deeper crater that extends trough the entire thickness of the surface epithelium and involves the underlying connective tissue WOOD AND GOAZ
Oral ulcers may be divided into 2 groupsShort term (those that usually disappear within 3 weeks) Persistent (last longer than 3 weeks)
WOOD AND GOAZ
Differential list of short term ulcers
Traumatic ulcer Recurrent aphthous ulcers-minor Recurrent intraoral herpes simplex Ulcer occurring as a result of odontogenic infection Ulcers occurring as a result of vesiculobullous diseases Ulcers secondary to infectious diseases WOOD AND GOAZ
Differential list of persistent ulcers
Traumatic ulcer Major aphthous ulcer Squamous cell carcinoma Ulcers in human immunodeficiency virus disease Low grade mucoepidermoid tumour Systemic mucosis Chancre Gumma WOOD AND GOAZ
Traumatic ulcer
Vary greatly in size and shape
Seldom are multiple or recurrent
On tongue,lips,mucobucc al fold,gingivae and palate WOOD AND GOAZ
Borders are raised and reddish
Bases may have yellowish white necrotic surface that may be readily removed
Frequently tender or regional lymphadenitis occurs as a result of contamination of the ulcer by oral flora WOOD AND GOAZ
Recurrent aphthous ulcer-minor
Shallow ulcer 0.5 to 2 cm in dia
Occur on movable mucosa (non keratinized) lips, buccal mucosa, tongue floor of mouth, mucobuccal fold , soft palate WOOD AND GOAZ
Yellow necrotic centre,smooth contoured border, red halo,symmetric and circular
Lesions occur singly , occasionally two or three and are widely distributed WOOD AND GOAZ
Recurrent intra oral herpes simplex Shallow ulcer,not more than 0.5 cm in dia with red halo,number of vesicles may occur in tight clusters,rupture to form lager ulcer upto 1.5 cm in dia Sclloped border
WOOD AND GOAZ
Lesion occurs on fixed mucosa , it is tightly bound to periosteum (keratinized) hard palate, gingivae, alveolar ridge
Lesion often returns to same location
WOOD AND GOAZ
Major aphthous ulcer Severe form of the minor RAU Usually single or at the most there are three Larger than 2 cm,deep very painful occur in the posterior of the mouth Heal with scar formation
WOOD AND GOAZ
Syphillis
Primary(chancre)-
Develop approximately 3 weeks after inoculation
single, indurated nonpainful ulcer at the site of sprirochete entry, spontaneously heals in 4-6 weeks. WOOD AND GOAZ
Oral lesions occur most often on lips, tip of tongue or gingiva
Measures 0.5 to 2 cm in dia,shallow ,oval or round in shape, have a narrow copper colored slightly raised borders with reddish brown base or centre regional lymph nodes are enlarged, firm discrete and painless
WOOD AND GOAZ
Secondarymaculopapular rash on skin
oral ulcers covered by mucous membrane(mucous patches)
WOOD AND GOAZ
Snail track ulcers-multiple small ,rounded superficial erosions which coalesce to form narrow curved shallow ulcers
Lymph nodes –enlarged and painless
S .DAS
3 Stage- gumma Occur most often In palate or tongue starting at small firm nodular masses
Necrosis commences within nodules and produces ulceration of surface epi
Necrotic tissue at the base of ulcer sloughs awaypunched out lesion is seen WOOD AND GOAZ
T.B
Oval in shape with irregular cresentric border Often multile
Slightly Indurated, chronic ulcer that may be painfulon any mucosal surface
Reddish blue Undermined edges
WOOD AND GOAZ
Ulcers from odontogenic infections
In most cases of chronic alveolar abscess, ulcer is seen on alveolar ridge on buccal or lingual surface near mucobuccal fold, seldom on palate
Pressure on adjacent soft tissues causes pus to exude from ulcer , Identifies the condition
S .DAS
A gutta percha point may be placed in the ulcer and ed into the tract as far as it will go without undue force radiograph is taken If the point is seen to reach the apex infected tooth diagnosis is ensured WOOD AND GOAZ
U O Y K THAN
Guided by: Dr. Munish Kumar Dr.Ravi Narula
Presented by: Amritveer Kaur
An ulcer is the break in the continuity of covering epithelium-skin or mucous membrane
Follow the molecular death of the covering epithelium or its traumatic removal
S .DAS
PARTS OF ULCER
Margin Edge Floor Base
S .DAS
CLASSIFICATION OF ULCERS • TWO TYPES OF CLASSIFICATON OF ULCERS IS POSSIBLE:1.
CLINICAL:
2.
PATHOLOGICAL
S .DAS
Callous/ Chronic
S .DAS
Arterial, Traumatic,
S .DAS
HISTORY
Mode of onset Duration Pain Discharge Associated disease
S .DAS
1) Mode of onset
How ulcer developed ??
Traumatic- Eg.dental ulcer of the tongue
Spontaneously- may develop following a swelling which may be matted tuberculous lymph node or gumma or a rapidly growing malignant tumour ( malignant melanoma)
S .DAS
Marjolins ulcer- on burn scar
S .DAS
2) DURATION
How long??
Acute ulcer,chronic ulcer
Incubation period-time interval between exposure and the onset
S .DAS
3) PAIN
IsInflammatory the ulcer painful?? ulcers
S .DAS
4) DISCHARGE
Does the ulcer discharge or not??
Nature of discharge-serum, pus or blood
S .DAS
5) ASSOCIATED DISEASE
Nervous diseases Tuberculosis Diabetes syphillis
S .DAS
LOCAL EXAMINATION
Inspection Palpation Lymph Nodes
S .DAS
A ) Inspection
Size & Shape Number Position Edge, Margin, Floor Discharge Surrounding area
S .DAS
1. Size & Shape Tuberculous
S .DAS
2. Number
Tuberculous ,gummatous,varicose ulcers and soft chancres may be more than one in number
S .DAS
3. Position RODENT ULCERS
S .DAS
Anywhere Over Where subcutaneous in the bones such as
S .DAS
4.EDGE
Area between the margin and the floor
An ulcer has a margin or edge which takes characteristic shape in a particular form of ulcer
Gives clue to the diagnosis of ulcer also to the condition of ulcer
S .DAS
TYPES OF EDGES
Undermined edges Punched out edges Sloping Raised and pearly white beaded Everted
S .DAS
UNDERMINED EDGES
Mostly seen in tuberculosis Subcutaneous tissue destroyed faster than skin Overlying skin is thin friable ,reddish blue and unhealthy
S .DAS
Undermining of edges
S .DAS
PUNCHED OUT EDGE
Gummatus ulcer or in deep trophic ulcer Edge drops down at right angles to skin surface Disease which causes the ulcer itself do not tend to spread to the surrounding tissue
S .DAS
Punched out ulcers as seen in vasculitis
S .DAS
SLOPING EDGE
Healing traumatic or venous ulcers Reddish purple in color Consists of new healthy epithelium
S .DAS
Healing traumatic ulcer
S .DAS
RAISED AND PEARLY WHITE BEADED EDGE
Rodent ulcer Develops in invasive cellular disease and becomes necrotic at centre
S .DAS
BCC WITH TYPICAL ROLLED PEARLY WHITE EDGES
S .DAS
ROLLED OUT EVERTED EDGE Squamous cell carcinoma or an ulcerated adenocarcinoma Caused by fast growing cellular disease , growing portion at the edge of ulcer heaps up and spills over normal skin to produce an everted edge
S .DAS
SCC BUCCAL MUCOSA
S .DAS
Healing ulcer- blue zone (growing spreading ulcer- edge is inflammed and oedematous epi) and a white zone (fibrosis) S .DAS
5.FLOOR
Exposed surface of the ulcer
When floor is covered with red granulation tissue ulcer seems to be healthy and healing
Pale and smooth granulation tissue-slowely healing ulcer
Wash leather slough-gummatous ulcer S .DAS
Trophic ulcer penetrates down even to the bone-which forms the floor in that case
A black mass at the floor suggests malignat melanoma
S .DAS
A black mass at floor suggests malignant melanoma S .DAS
6.Discharge
Character
Its amount and smell
Healing ulcer-scanty serous discharge
Spreading and inflammed ulcer-purulent discharge
Malignant ulcer-sero-sanguineous discharge S .DAS
7. Surrounding area
glossy ,red and oedematous Acutely inflammed-
Scar or wrinkling – old case of tuberculosis
Dark pigmentation & eczema → varicose ulcer
Hypopigmentation → non-healing ulcer
S .DAS
B. PALPATION
Tenderness Edge and margin Base Depth Bleeding Relations to deeper structures Surrounding skin
S .DAS
1. Tenderness Acutely
S .DAS
2. Edge and margin
Marked Induration-squamous cell carcinoma
Slight induration- chronic ulcer
S .DAS
3. Base
On which the ulcer rests Better felt than seen
If an attempt is made to lift the ulcer between the thumb and index finger, base will be felt
Slight induration at the base-chronic ulcer Marked induration (hardness)-squamous cell carcinoma
S .DAS
Relations to deeper structures
Gummatous ulcer over subcutaneous bone (tibia,sternum) –often fixed Malignant also fixed
S .DAS
Surrounding skin
temperature & tenderness Mobility Fixity to deeper structure –malignant lesion For nerve lesion
S .DAS
C.EXAMINATION OF LYMPH NODES
Acute ulcers –regional lymph nodes enlarged tender
Tuberculous ulcers-enlarged ,matted ,slightly tender
Malignant ulcers-stony hard and fixed
S .DAS
SPECIAL INVESTIGATIONS
Routine blood examination Bacteriological examination of the discharge Chest X-Ray Biopsy
S .DAS
ORAL ULCERS
Erosion / Ulcer
Erosion –shallow crater in the epithelial surface , erythematous area, implies only superficial damage
Ulcer –deeper crater that extends trough the entire thickness of the surface epithelium and involves the underlying connective tissue WOOD AND GOAZ
Oral ulcers may be divided into 2 groupsShort term (those that usually disappear within 3 weeks) Persistent (last longer than 3 weeks)
WOOD AND GOAZ
Differential list of short term ulcers
Traumatic ulcer Recurrent aphthous ulcers-minor Recurrent intraoral herpes simplex Ulcer occurring as a result of odontogenic infection Ulcers occurring as a result of vesiculobullous diseases Ulcers secondary to infectious diseases WOOD AND GOAZ
Differential list of persistent ulcers
Traumatic ulcer Major aphthous ulcer Squamous cell carcinoma Ulcers in human immunodeficiency virus disease Low grade mucoepidermoid tumour Systemic mucosis Chancre Gumma WOOD AND GOAZ
Traumatic ulcer
Vary greatly in size and shape
Seldom are multiple or recurrent
On tongue,lips,mucobucc al fold,gingivae and palate WOOD AND GOAZ
Borders are raised and reddish
Bases may have yellowish white necrotic surface that may be readily removed
Frequently tender or regional lymphadenitis occurs as a result of contamination of the ulcer by oral flora WOOD AND GOAZ
Recurrent aphthous ulcer-minor
Shallow ulcer 0.5 to 2 cm in dia
Occur on movable mucosa (non keratinized) lips, buccal mucosa, tongue floor of mouth, mucobuccal fold , soft palate WOOD AND GOAZ
Yellow necrotic centre,smooth contoured border, red halo,symmetric and circular
Lesions occur singly , occasionally two or three and are widely distributed WOOD AND GOAZ
Recurrent intra oral herpes simplex Shallow ulcer,not more than 0.5 cm in dia with red halo,number of vesicles may occur in tight clusters,rupture to form lager ulcer upto 1.5 cm in dia Sclloped border
WOOD AND GOAZ
Lesion occurs on fixed mucosa , it is tightly bound to periosteum (keratinized) hard palate, gingivae, alveolar ridge
Lesion often returns to same location
WOOD AND GOAZ
Major aphthous ulcer Severe form of the minor RAU Usually single or at the most there are three Larger than 2 cm,deep very painful occur in the posterior of the mouth Heal with scar formation
WOOD AND GOAZ
Syphillis
Primary(chancre)-
Develop approximately 3 weeks after inoculation
single, indurated nonpainful ulcer at the site of sprirochete entry, spontaneously heals in 4-6 weeks. WOOD AND GOAZ
Oral lesions occur most often on lips, tip of tongue or gingiva
Measures 0.5 to 2 cm in dia,shallow ,oval or round in shape, have a narrow copper colored slightly raised borders with reddish brown base or centre regional lymph nodes are enlarged, firm discrete and painless
WOOD AND GOAZ
Secondarymaculopapular rash on skin
oral ulcers covered by mucous membrane(mucous patches)
WOOD AND GOAZ
Snail track ulcers-multiple small ,rounded superficial erosions which coalesce to form narrow curved shallow ulcers
Lymph nodes –enlarged and painless
S .DAS
3 Stage- gumma Occur most often In palate or tongue starting at small firm nodular masses
Necrosis commences within nodules and produces ulceration of surface epi
Necrotic tissue at the base of ulcer sloughs awaypunched out lesion is seen WOOD AND GOAZ
T.B
Oval in shape with irregular cresentric border Often multile
Slightly Indurated, chronic ulcer that may be painfulon any mucosal surface
Reddish blue Undermined edges
WOOD AND GOAZ
Ulcers from odontogenic infections
In most cases of chronic alveolar abscess, ulcer is seen on alveolar ridge on buccal or lingual surface near mucobuccal fold, seldom on palate
Pressure on adjacent soft tissues causes pus to exude from ulcer , Identifies the condition
S .DAS
A gutta percha point may be placed in the ulcer and ed into the tract as far as it will go without undue force radiograph is taken If the point is seen to reach the apex infected tooth diagnosis is ensured WOOD AND GOAZ
U O Y K THAN