Fmcg Characteristics 6g1b6v
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Fmcg Characteristics as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 614
- Pages: 2
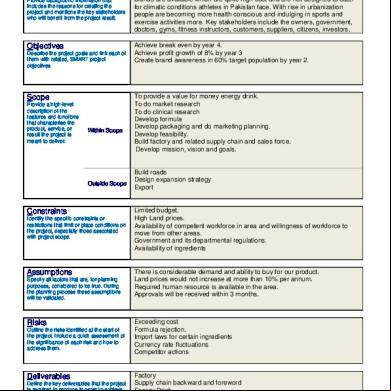
FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (F.M.C.G.) 2.1 – INDUSTRY PROFILE INTRODUCTION: Products which have a quick turnover, and relatively low cost are known as Fast Moving Consumer Goods (F.M.C.G.). F.M.C.G. products are those that get replaced within a year. Examples of F.M.C.G. generally include a wide range of frequently purchased consumer products such as toiletries, soap, cosmetics, tooth cleaning products, shaving products and detergents, as well as other non-durables such as glassware, bulbs, batteries, paper products, and plastic goods. F.M.C.G. may also include pharmaceuticals, consumer electronics, packaged food products, soft drinks, tissue paper, and chocolate bars. India’s F.M.C.G. sector is the fourth largest sector in the economy and creates employment for more than three million people in downstream activities. Its principal constituents are Household Care, Personal Care and Food & Beverages. The total F.M.C.G. market is in excess of Rs. 85,000 Crores. It is currently growing at double digit growth rate and is expected to maintain a high growth rate. F.M.C.G. Industry is characterized by a well established distribution network, low penetration levels, low operating cost, lower per capita consumption and intense competition between the organized and unorganized segments. 2.1.1 HISTORY OF F.M.C.G. IN INDIA: In India, companies like ITC, H.U.L., Colgate, Cadbury and Nestle have been a dominant force in the F.M.C.G. sector well ed by relatively less competition and high entry barriers (import duty was high). These companies were, therefore, able to charge a for their products. In this context, the margins were also on the higher side. With the gradual opening up of the economy over the last decade, F.M.C.G. companies have been forced to fight for a market share. In the process, margins have been compromised.
FMCG Characteristics
Fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) – or Consumer Packaged Goods (G) – are products that are sold quickly and at relatively low cost. Examples include non-durable goods such as soft drinks, toiletries, and grocery items.[1] Though the absolute profit made on FMCG products is relatively small, they generally sell in large quantities, so the cumulative profit on such products can be large. The term FMCG refers to those retail goods that are generally replaced or fully used up over a short period of days, weeks, or months, and within one year.This contrasts with durable goods or major appliances such as kitchen appliances, which are generally replaced over a period of several years.
FMCGs have a short shelf life, either as a result of high consumer demand or because the product deteriorates rapidly. Some FMCGs – such as meat, fruits and vegetables, dairy products and baked goods – are highly perishable. Other goods such as alcohol, toiletries, pre-packaged foods, soft drinks and cleaning products have high turnover rates. The following are the main characteristics of FMCGs:[1] From the consumers' perspective: Frequent purchase Low involvement (little or no effort to choose the item -- products with strong brand loyalty are exceptions to this rule) Low price From the marketers' angle: High volumes Low contribution margins Extensive distribution networks High stock turnover
====
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) goods are all consumable items (other than groceries/pulses) that one needs to buy at regular intervals. These are items which are used daily, and so have a quick rate of consumption, and a high return. FMCG can broadly be categorized into three segments which are: 1. Household items as soaps, detergents, household accessories, etc, 2. Personal care items as shampoos, toothpaste, shaving products, etc and finally 3. Food and Beverages as snacks, processed foods, tea, coffee, edible oils, soft drinks etc. Global leaders in the FMCG segment are Nestlé, ITC, Hindustan Unilever Limited, Reckitt Benckiser, Unilever, Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, Carlsberg, Kleenex, General Mills, Pepsi, Gillette etc.
FMCG Characteristics
Fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) – or Consumer Packaged Goods (G) – are products that are sold quickly and at relatively low cost. Examples include non-durable goods such as soft drinks, toiletries, and grocery items.[1] Though the absolute profit made on FMCG products is relatively small, they generally sell in large quantities, so the cumulative profit on such products can be large. The term FMCG refers to those retail goods that are generally replaced or fully used up over a short period of days, weeks, or months, and within one year.This contrasts with durable goods or major appliances such as kitchen appliances, which are generally replaced over a period of several years.
FMCGs have a short shelf life, either as a result of high consumer demand or because the product deteriorates rapidly. Some FMCGs – such as meat, fruits and vegetables, dairy products and baked goods – are highly perishable. Other goods such as alcohol, toiletries, pre-packaged foods, soft drinks and cleaning products have high turnover rates. The following are the main characteristics of FMCGs:[1] From the consumers' perspective: Frequent purchase Low involvement (little or no effort to choose the item -- products with strong brand loyalty are exceptions to this rule) Low price From the marketers' angle: High volumes Low contribution margins Extensive distribution networks High stock turnover
====
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) goods are all consumable items (other than groceries/pulses) that one needs to buy at regular intervals. These are items which are used daily, and so have a quick rate of consumption, and a high return. FMCG can broadly be categorized into three segments which are: 1. Household items as soaps, detergents, household accessories, etc, 2. Personal care items as shampoos, toothpaste, shaving products, etc and finally 3. Food and Beverages as snacks, processed foods, tea, coffee, edible oils, soft drinks etc. Global leaders in the FMCG segment are Nestlé, ITC, Hindustan Unilever Limited, Reckitt Benckiser, Unilever, Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, Carlsberg, Kleenex, General Mills, Pepsi, Gillette etc.