Islamic Economic Finance Course Outline 6or4p
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Islamic Economic Finance Course Outline as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 1,136
- Pages: 4
1.
Name of Course
2. 3.
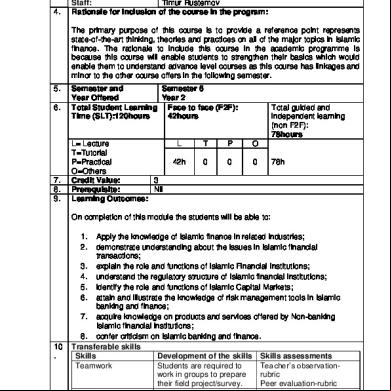
Course Code: Names of Academic Mohsin Ali Staff: Timur Rustemov Rationale for inclusion of the course in the program:
4.
Islamic Economics & Finance 2
The primary purpose of this course is to provide a reference point represents state-of-the-art thinking, theories and practices on all of the major topics in Islamic finance. The rationale to include this course in the academic programme is because this course will enable students to strengthen their basics which would enable them to understand advance level courses as this course has linkages and minor to the other course offers in the following semester. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9.
Semester and Semester 6 Year Offered Year 2 Total Student Learning Face to face (F2F): Time (SLT):120hours 42hours
L= Lecture T=Tutorial P=Practical O=Others Credit Value: 3 Prerequisite: Nil Learning Outcomes:
Total guided and independent learning (non F2F): 78hours
L
T
P
O
42h
0
0
0
78h
On completion of this module the students will be able to: 1. 2.
10 .
Apply the knowledge of Islamic finance in related industries; demonstrate understanding about the issues in Islamic financial transactions; 3. explain the role and functions of Islamic Financial Institutions; 4. understand the regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions; 5. identify the role and functions of Islamic Capital Markets; 6. attain and illustrate the knowledge of risk management tools in Islamic banking and finance; 7. acquire knowledge on products and services offered by Non-banking Islamic financial institutions; 8. confer criticism on Islamic banking and finance. Transferable skills Skills Development of the skills Skills assessments Teamwork Students are required to Teacher’s observationwork in groups to prepare rubric their field project/survey. Peer evaluation-rubric Participation& Written and Teacher’s observation Communication communications-via written Skills and presenting their field
1
project/survey. 11 .
Teaching-learning strategy Teaching and learning will be via lecture and discussion. Students are also required to do their own self-study through guided projects, assignments and homework activities. Assessment strategy: The assessment consists of assignments, presentations, quizzes, participation during classes and examinations.
12 .
13 . 14 .
15 .
Synopsis Studying Islamic finance is important for the dual purpose of having better sustenance and religious imperatives. Islam does not like the concept of the “pious person” as distinct from the “worldly person”. It ens a system of devotions/worship as well as guides on the economy, political affairs and international relations. Mode of Delivery Lecture; Class Discussion and Self-study. Assessment Methods and Types Mid-term Examination 20% Group Project 20% Presentation 10% Quizzes 10% Final Exam 40% Total 100% Mapping of the Course to the Program Aims Course
PEO1 PEO2 PEO3 PEO4 PEO5
Islamic Finance 16 .
X
X
X
X
X
Mapping of the course to the Program Learning Outcomes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CO 1 CO 2 CO 3 CO 4 CO 5 CO 6 CO 7 CO 8
PLO 1
PLO 2
PLO 3
X X
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
X X
Topic
PLO 4
PLO 5
X X
PLO 6
X X
X X X
F2F
PLO 7
PLO 8
X X X
X
X X X
X
X X
X
Non
SLT 2
L 4
F2F 8
12
6
12
18
3
2.1 Financial Instruments in use 2.2 Issues in contemporary sale contracts 2.3 Issues in lease contract 2.4 Agency problem in Mudharabah contract 2.5 Application & Concept of Waad, Waadan and Muawadah 2.6 Hybrid contracts in Islamic finance – Issues, application and challenges 2.7 Fiat Money vs Gold Dinar Overview of Islamic financial institutions
5
12
17
43.
3.1 Importance/Need of bank Transaction cost Asymmetric information Lender of last resort 3.2 Islamic Financial institutions and markets Islamic banks Islamic capital market – Islamic money market, Sukuk market and equity market Takaful and Re-takaful 3.3 Foreign exchange market in the Islamic framework 3.4 Derivatives for hedging purposes – Issues and challenges 3.5 Islamic alternatives to conventional derivative instrument Islamic Currency forward Islamic Profit rate swap 3.6 Insurable interest and its application in Takaful 3.7 Microfinance 3.8 Comparison between Islamic and conventional microfinance Regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions
6
10
16
1 1.
An Overview Of Islamic finance
1.1 Introduction of Shariah 1.2 Maqasid al Shariah 1.3 Introduction to Islamic economic system Ownership and property rights Laissez faire economy Factors of production 1.4 Distinguishing features of Islamic finance Basic prohibitions Business ethics and norms 1.5 Prohibition of interest in major religions 1.6 Pillars of contracts and sources of prohibitions 1.7 Role of Islamic bank as a financial intermediary 1.8 Concept of Legitimate profit in Islam 2 2. Issues in Islamic financial instruments
T
P
O
4.1 Justification/Need for the regulation 4.2 Regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions AAOIFI standards IFSB guidelines for CAR IFSB guidelines on corporate governance 4.4 Comparison of BASEL and IFSB CAR 4.3 Role and functions of Shariah supervisory board Issue of confidentiality Issue of independence
3
54.
Issue of competency 4.4 Legal framework of Islamic financial industry in Malaysia Islamic capital market
6
10
16
6
5.1 Classification of capital market 5.2 Introduction to Islamic debt market 5.3 Sukuk – concept, various structures and their applications 5.4 Tradability of Sukuk – Issue of Bai Dayn 5.5 Other vital issues in Sukuk such as and structure of Sukuk 5.6 Stock screening criteria Qualitative screening Quantitative screening 5.7 Short selling – Concepts and issues Risk management in Islamic financial institutions
6
10
16
7
6.1 Definition and concept of risk management 6.2 Risk management from Islamic perspective – Evidence from Quran and Sunnah 6.3 Risks faced by Islamic financial institutions 6.4 Importance of Operational risk in Islamic banks 6.5 Unique risks faced by Islamic banks 6.6 Derivatives – Importance, necessity and Issues 6.7 Islamic derivate instruments – Structure and its application 6.8 Need for financial engineering in Islamic finance Non-Banking Financial Institutions
6
10
16
8
7.1 Takaful 7.2 Retakaful 7.3 Fund Management Companies 7.4 Pension Funds 7.5 Unit Trust 7.6 Exchange Traded Funds 7.7 Importance in Islamic Finance Sphere Criticism of Islamic banking and finance
3
6
9
42
78
120
8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4
Time value of money and Islamic banking Divergence between theory and Practice Islamic banks to act as Social welfare institutions? The way forward
TOTAL Student Learning Time (h) Reference:
1. Asyraf Wajdi (Editor), Islamic Financial System: Principles & Operations, ISRA 2. Zamir Iqbal and Abbas Mirakhor, (2011) An Introduction to Islamic finance, nd Theory and Practice, 2 edition, John Wiley and Sons. 3. Ayub, Muhammad (2007). Understanding Islamic Finance. John Wiley & Sons. 4. Mahmoud A. El –Gamal (2006), Islamic finance – Law, Economics and Practice, Cambridge University Press
4
Name of Course
2. 3.
Course Code: Names of Academic Mohsin Ali Staff: Timur Rustemov Rationale for inclusion of the course in the program:
4.
Islamic Economics & Finance 2
The primary purpose of this course is to provide a reference point represents state-of-the-art thinking, theories and practices on all of the major topics in Islamic finance. The rationale to include this course in the academic programme is because this course will enable students to strengthen their basics which would enable them to understand advance level courses as this course has linkages and minor to the other course offers in the following semester. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9.
Semester and Semester 6 Year Offered Year 2 Total Student Learning Face to face (F2F): Time (SLT):120hours 42hours
L= Lecture T=Tutorial P=Practical O=Others Credit Value: 3 Prerequisite: Nil Learning Outcomes:
Total guided and independent learning (non F2F): 78hours
L
T
P
O
42h
0
0
0
78h
On completion of this module the students will be able to: 1. 2.
10 .
Apply the knowledge of Islamic finance in related industries; demonstrate understanding about the issues in Islamic financial transactions; 3. explain the role and functions of Islamic Financial Institutions; 4. understand the regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions; 5. identify the role and functions of Islamic Capital Markets; 6. attain and illustrate the knowledge of risk management tools in Islamic banking and finance; 7. acquire knowledge on products and services offered by Non-banking Islamic financial institutions; 8. confer criticism on Islamic banking and finance. Transferable skills Skills Development of the skills Skills assessments Teamwork Students are required to Teacher’s observationwork in groups to prepare rubric their field project/survey. Peer evaluation-rubric Participation& Written and Teacher’s observation Communication communications-via written Skills and presenting their field
1
project/survey. 11 .
Teaching-learning strategy Teaching and learning will be via lecture and discussion. Students are also required to do their own self-study through guided projects, assignments and homework activities. Assessment strategy: The assessment consists of assignments, presentations, quizzes, participation during classes and examinations.
12 .
13 . 14 .
15 .
Synopsis Studying Islamic finance is important for the dual purpose of having better sustenance and religious imperatives. Islam does not like the concept of the “pious person” as distinct from the “worldly person”. It ens a system of devotions/worship as well as guides on the economy, political affairs and international relations. Mode of Delivery Lecture; Class Discussion and Self-study. Assessment Methods and Types Mid-term Examination 20% Group Project 20% Presentation 10% Quizzes 10% Final Exam 40% Total 100% Mapping of the Course to the Program Aims Course
PEO1 PEO2 PEO3 PEO4 PEO5
Islamic Finance 16 .
X
X
X
X
X
Mapping of the course to the Program Learning Outcomes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CO 1 CO 2 CO 3 CO 4 CO 5 CO 6 CO 7 CO 8
PLO 1
PLO 2
PLO 3
X X
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
X X
Topic
PLO 4
PLO 5
X X
PLO 6
X X
X X X
F2F
PLO 7
PLO 8
X X X
X
X X X
X
X X
X
Non
SLT 2
L 4
F2F 8
12
6
12
18
3
2.1 Financial Instruments in use 2.2 Issues in contemporary sale contracts 2.3 Issues in lease contract 2.4 Agency problem in Mudharabah contract 2.5 Application & Concept of Waad, Waadan and Muawadah 2.6 Hybrid contracts in Islamic finance – Issues, application and challenges 2.7 Fiat Money vs Gold Dinar Overview of Islamic financial institutions
5
12
17
43.
3.1 Importance/Need of bank Transaction cost Asymmetric information Lender of last resort 3.2 Islamic Financial institutions and markets Islamic banks Islamic capital market – Islamic money market, Sukuk market and equity market Takaful and Re-takaful 3.3 Foreign exchange market in the Islamic framework 3.4 Derivatives for hedging purposes – Issues and challenges 3.5 Islamic alternatives to conventional derivative instrument Islamic Currency forward Islamic Profit rate swap 3.6 Insurable interest and its application in Takaful 3.7 Microfinance 3.8 Comparison between Islamic and conventional microfinance Regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions
6
10
16
1 1.
An Overview Of Islamic finance
1.1 Introduction of Shariah 1.2 Maqasid al Shariah 1.3 Introduction to Islamic economic system Ownership and property rights Laissez faire economy Factors of production 1.4 Distinguishing features of Islamic finance Basic prohibitions Business ethics and norms 1.5 Prohibition of interest in major religions 1.6 Pillars of contracts and sources of prohibitions 1.7 Role of Islamic bank as a financial intermediary 1.8 Concept of Legitimate profit in Islam 2 2. Issues in Islamic financial instruments
T
P
O
4.1 Justification/Need for the regulation 4.2 Regulatory structure of Islamic financial institutions AAOIFI standards IFSB guidelines for CAR IFSB guidelines on corporate governance 4.4 Comparison of BASEL and IFSB CAR 4.3 Role and functions of Shariah supervisory board Issue of confidentiality Issue of independence
3
54.
Issue of competency 4.4 Legal framework of Islamic financial industry in Malaysia Islamic capital market
6
10
16
6
5.1 Classification of capital market 5.2 Introduction to Islamic debt market 5.3 Sukuk – concept, various structures and their applications 5.4 Tradability of Sukuk – Issue of Bai Dayn 5.5 Other vital issues in Sukuk such as and structure of Sukuk 5.6 Stock screening criteria Qualitative screening Quantitative screening 5.7 Short selling – Concepts and issues Risk management in Islamic financial institutions
6
10
16
7
6.1 Definition and concept of risk management 6.2 Risk management from Islamic perspective – Evidence from Quran and Sunnah 6.3 Risks faced by Islamic financial institutions 6.4 Importance of Operational risk in Islamic banks 6.5 Unique risks faced by Islamic banks 6.6 Derivatives – Importance, necessity and Issues 6.7 Islamic derivate instruments – Structure and its application 6.8 Need for financial engineering in Islamic finance Non-Banking Financial Institutions
6
10
16
8
7.1 Takaful 7.2 Retakaful 7.3 Fund Management Companies 7.4 Pension Funds 7.5 Unit Trust 7.6 Exchange Traded Funds 7.7 Importance in Islamic Finance Sphere Criticism of Islamic banking and finance
3
6
9
42
78
120
8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4
Time value of money and Islamic banking Divergence between theory and Practice Islamic banks to act as Social welfare institutions? The way forward
TOTAL Student Learning Time (h) Reference:
1. Asyraf Wajdi (Editor), Islamic Financial System: Principles & Operations, ISRA 2. Zamir Iqbal and Abbas Mirakhor, (2011) An Introduction to Islamic finance, nd Theory and Practice, 2 edition, John Wiley and Sons. 3. Ayub, Muhammad (2007). Understanding Islamic Finance. John Wiley & Sons. 4. Mahmoud A. El –Gamal (2006), Islamic finance – Law, Economics and Practice, Cambridge University Press
4