Methyl Benzoate 3u514u
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Methyl Benzoate as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 782
- Pages: 4
Laboratory Report: Chemistry 2311-1L Our Lady of the Lake College Pre-Lab Name: Tevin Erlambang Partner Name: Kirstie Bridges Date: I. Title: Nitration of Methyl Benzoate, a Macroscale Synthesis II. Objective (one sentence): To perform a reaction on a macroscale, run a reaction with concentrated acids, understand the link between reaction temperature and control of reaction path, and identify and determine purity of the product based on spectroscopic methods. III. Table of Chemicals: Name
Formula/ Structure (must be drawn)
Hazards
PPE
Nitric acid
HNO3
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Methyl benzoate
C8H8O2
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Methanol
CH3OH
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Spring 2015
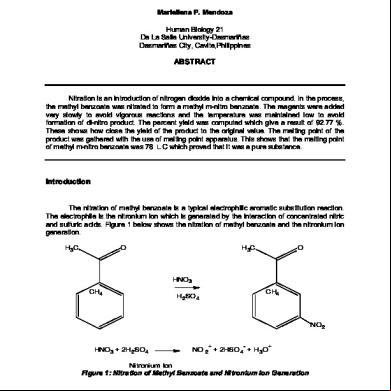
IV. Procedure (cited procedure only): See "Procedure" section of the experiment, Nitration of Methyl Benzoate, a Macroscale Synthesis. V. Observations (no more than one paragraph, 5-10 sentences): When we put the reaction mixture into the ice, it turned into a milky color and the product began to precipitate. The crude products showed a huge peak at meta and minor peaks at ortho and para which are impurity peaks. The larger impurity peak being the ortho and the smaller one being para. The weight of our product was 4.91g. Our theoretical yield was 6.528g. and our percent yield was 75.21%. VI. Calculations (if applicable) (must be written): Product= 4.91g of methyl m-nitrobenzoate Density of methyl benzoate= 1.088 g/mL Theoretical yield: (6 mL methyl benzoate) x (1.088 g/ 1mL)= 6.528g m-nitrobenzoate Percent yield: (4.91g / 6.528g) x100= 75.21% VII. Discussion and Conclusions (no more than one paragraph, 5-10 sentences): We were able to conclude that meta was our main product and ortho and para were minor products based on their retention times. Meta had a retention time of 11.495 minutes, where as the ortho was at 10.509 minutes and para was at 10.952 minutes. I believe that our percent yield was pretty good! Since it was 75.21% it shows that our reaction was efficient. VIII. Post-Lab Questions (copy and paste directly from the labs posted in Moodle) 1. Write the chemical reaction showing how the electrophile for the nitration of methyl benzoate was formed.
2. Why does methyl benzoate, which is insoluble, dissolve in concentrated H2SO4? Sulfuric acid can protonate the carboxyl group of the methyl benzoate, which produces an ionic species which is soluble in the polar sulfuric acid. Now that the methyl benzoate has a positive charge it will be able to dissolve in polar sulfuric acid. 3. In the nitration of methyl benzoate, yields of product were moderate at best. Which undesired products may have formed which would have lowered the yields? What
Spring 2015
procedural error may have led to these products?
4. The nitrosubstituent was introduced in the meta position of the methyl benzoate. Why does it preferentially occur at meta, other than para or ortho? Because the methyl ester group is a meta-director and the main product is methyl m-nitrobenzoate. 5. Calculate the percent yield and percent recovery for today's reaction? The percent yield was 75.21% & percent recovery. 6. Label the IR and NMR spectra obtained in the lab. Does the final spectrum indicate product? Why? Identify any impurities in spectra and suggest methods for removing these impurities. Can you tell if your product is dinitrated from the IR? The crude products showed a huge peak at meta and minor peaks at ortho and para which are impurity peaks. The larger impurity peak being the ortho and the smaller one being para 7. During the procedure, several washes with cold methanol were done. Why is it important to use cold methanol? Our product is slightly soluble in cold
methanol and more soluble in hot methanol. Cold methanol dissolves less product than warm/hot methanol.
Spring 2015
8. Why is it important to use a minimal amount of methanol for recrystallization? . If you use large amounts of cold methanol to wash your product, you will lower your yield as the methanol will dissolve some of your product and carry it through the filter. 9. What removes the hydrogen from the sp3 carbon in the cationic reaction intermediate to allow the aromatic ring to reform? in an aromatic nitration, the nitrating species is a nitronium ion, NO2+ formed when sulfuric acid protonates HNO3 and takes away water. The molecule that removes the proton from the sigma complex (cationic species) would be the best base in the reaction mixture, This is NOT NO3-, HSO4- or SO4-2. The best base is water.
Spring 2015
Formula/ Structure (must be drawn)
Hazards
PPE
Nitric acid
HNO3
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Methyl benzoate
C8H8O2
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Methanol
CH3OH
Skin and eye irritant, Splash goggles. ingestion and Lab coat, gloves inhalation hazard
Spring 2015
IV. Procedure (cited procedure only): See "Procedure" section of the experiment, Nitration of Methyl Benzoate, a Macroscale Synthesis. V. Observations (no more than one paragraph, 5-10 sentences): When we put the reaction mixture into the ice, it turned into a milky color and the product began to precipitate. The crude products showed a huge peak at meta and minor peaks at ortho and para which are impurity peaks. The larger impurity peak being the ortho and the smaller one being para. The weight of our product was 4.91g. Our theoretical yield was 6.528g. and our percent yield was 75.21%. VI. Calculations (if applicable) (must be written): Product= 4.91g of methyl m-nitrobenzoate Density of methyl benzoate= 1.088 g/mL Theoretical yield: (6 mL methyl benzoate) x (1.088 g/ 1mL)= 6.528g m-nitrobenzoate Percent yield: (4.91g / 6.528g) x100= 75.21% VII. Discussion and Conclusions (no more than one paragraph, 5-10 sentences): We were able to conclude that meta was our main product and ortho and para were minor products based on their retention times. Meta had a retention time of 11.495 minutes, where as the ortho was at 10.509 minutes and para was at 10.952 minutes. I believe that our percent yield was pretty good! Since it was 75.21% it shows that our reaction was efficient. VIII. Post-Lab Questions (copy and paste directly from the labs posted in Moodle) 1. Write the chemical reaction showing how the electrophile for the nitration of methyl benzoate was formed.
2. Why does methyl benzoate, which is insoluble, dissolve in concentrated H2SO4? Sulfuric acid can protonate the carboxyl group of the methyl benzoate, which produces an ionic species which is soluble in the polar sulfuric acid. Now that the methyl benzoate has a positive charge it will be able to dissolve in polar sulfuric acid. 3. In the nitration of methyl benzoate, yields of product were moderate at best. Which undesired products may have formed which would have lowered the yields? What
Spring 2015
procedural error may have led to these products?
4. The nitrosubstituent was introduced in the meta position of the methyl benzoate. Why does it preferentially occur at meta, other than para or ortho? Because the methyl ester group is a meta-director and the main product is methyl m-nitrobenzoate. 5. Calculate the percent yield and percent recovery for today's reaction? The percent yield was 75.21% & percent recovery. 6. Label the IR and NMR spectra obtained in the lab. Does the final spectrum indicate product? Why? Identify any impurities in spectra and suggest methods for removing these impurities. Can you tell if your product is dinitrated from the IR? The crude products showed a huge peak at meta and minor peaks at ortho and para which are impurity peaks. The larger impurity peak being the ortho and the smaller one being para 7. During the procedure, several washes with cold methanol were done. Why is it important to use cold methanol? Our product is slightly soluble in cold
methanol and more soluble in hot methanol. Cold methanol dissolves less product than warm/hot methanol.
Spring 2015
8. Why is it important to use a minimal amount of methanol for recrystallization? . If you use large amounts of cold methanol to wash your product, you will lower your yield as the methanol will dissolve some of your product and carry it through the filter. 9. What removes the hydrogen from the sp3 carbon in the cationic reaction intermediate to allow the aromatic ring to reform? in an aromatic nitration, the nitrating species is a nitronium ion, NO2+ formed when sulfuric acid protonates HNO3 and takes away water. The molecule that removes the proton from the sigma complex (cationic species) would be the best base in the reaction mixture, This is NOT NO3-, HSO4- or SO4-2. The best base is water.
Spring 2015