Ec302 h1m22
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
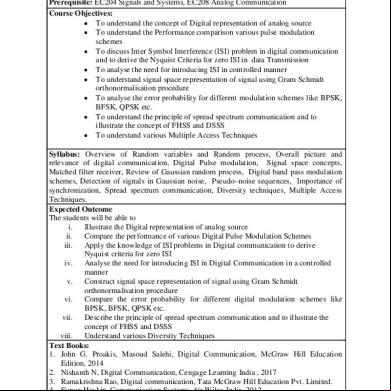
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Ec302 as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 645
- Pages: 24
Department of Technical Education Andhra Pradesh Name
: R.Rama Rao
Designation
: Lecturer.
Branch
: Electronics & Communication Engineering.
Institute
: Govt. Polytechnic (w), Bheemunipatnam,
Year/Semester
: Third Semester.
Subject
: Electronics circuits-1
Subject Code
: E.C-302
Topic
: Transistor Amplifiers.
Duration
: 50min.
Sub-Topic
: Thermistor & Sensistor Compensation techniques.
Teaching Aid
: PPT.
EC302.30
1
RECAP Earlier we have studied about
•
Need for compensation.
•
Types of bias compensation.
•
Diode compensation. EC302.30
2
OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this period you would be able to understand
• Thermistor compensation.
• Sensistor compensation.
EC302.30
3
•What is a Thermister? Thermister is a device which is having negative temperature coefficient
•What is a sensistor? Sensistor is a device which is having positive temperature coefficient
EC302.30
4
THERMISTOR COMPENSATION
EC302.30
5
Thermistor compensation circuit Fig. 1 EC302.30
6
Working • Circuit shows thermistor compensation in a self – bias CE amplifier. • The thermistor RT has negative temperature coefficient. • Negative temparature coefficient means resistance decreases exponentially with increse in temparature T. EC302.30
7
Thermistor can be placed in any one of the two positions as shown in Fig Thermister RT is used to minimize the increase in collector current due to variations in ICO , VBE or β with temperature .
EC302.30
8
If the temparature increases •
Thermistor resistance decreases.
•
Current flowing through RT (IT) increases.
•
Since the voltage drop across RE increases in the direction, it reverse biases the transistor Base –Emitter
junction which reduces IBand keeps IC constant. •
Thus RT compensates the increase in IC due to temperature rise.
EC302.30
9
The process is as follows • Increases VE • Reduces VBE • VBE = VB - VE • VBE = VCC X R2 / (R1+R2) (fixed) • IB decreases • IC remains constant
EC302.30
10
• Thus the temperature sensitivity of RT provides compensation to the increase in collector current IC due to rise in temperature T. • The same result is obtained if the transistor RT is placed in the base circuit across R2 instead of in collector circuit.
EC302.30
11
SENSISTOR COMPENSATION
EC302.30
12
Sensistor compensation circuit Fig.1 EC302.30
13
•
Instead of thermistor compensation, compensation can be done by using sensistor.
•
Sensistor is a temperature sensitive device.
•
Sensistor has positive temperature coefficient.
•
Sensistor is a heavily doped semi conductor. EC302.30
14
Generally sensistors have
• Temperature coefficient of resistance of 0.007 per 0C
• The range of temperature from - 600 0C to 1500 0C.
EC302.30
15
•
The sensistor may be placed either in parallel with R1.
•
Or in parallel with RE
•
The sensistor can also be placed in place of RE rather than in parallel with RE. EC302.30
16
With the increase in temperature •
The resistance of RS increases.
•
So, the resistance of parallel combination (RS || R1) increases.
•
Hence voltage drop across R2 decreases.
•
VR2 = VCC*(R2 / (R1||RS) + R2)
EC302.30
17
•
Decrease in VR2 decreases the net forward emitter Bias (VBE).
•
Hence Collector current IC decreases.
EC302.30
18
•
Decrease in IC compensates the increase in collector current IC due to increase in IC0 ,β or VBE because of temperature rise.
EC302.30
19
Summary •
We have discussed the circuits using thermistors & sensistors.
•
The circuits stabilize IC against variations in ICO,β & VBE due to rise in temperature.
EC302.30
20
Quiz 1.
If the temperature increases, thermistor resistance A)
Increases
B)
Decreases
C) Constant D) Zero
EC302.30
21
•
In compensation the value IC must be A)
Decreased
B.
Increased
C) Constant D)
Zero
EC302.30
22
1.
If the temperature increase, sensistor resistance
A) Increases B) Decreases C) Constant D) Zero
EC302.30
23
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
•
Explain with circuit diagram the thermistor compensation?
•
Explain with circuit diagram the sensistor compensation?
EC302.30
24
: R.Rama Rao
Designation
: Lecturer.
Branch
: Electronics & Communication Engineering.
Institute
: Govt. Polytechnic (w), Bheemunipatnam,
Year/Semester
: Third Semester.
Subject
: Electronics circuits-1
Subject Code
: E.C-302
Topic
: Transistor Amplifiers.
Duration
: 50min.
Sub-Topic
: Thermistor & Sensistor Compensation techniques.
Teaching Aid
: PPT.
EC302.30
1
RECAP Earlier we have studied about
•
Need for compensation.
•
Types of bias compensation.
•
Diode compensation. EC302.30
2
OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this period you would be able to understand
• Thermistor compensation.
• Sensistor compensation.
EC302.30
3
•What is a Thermister? Thermister is a device which is having negative temperature coefficient
•What is a sensistor? Sensistor is a device which is having positive temperature coefficient
EC302.30
4
THERMISTOR COMPENSATION
EC302.30
5
Thermistor compensation circuit Fig. 1 EC302.30
6
Working • Circuit shows thermistor compensation in a self – bias CE amplifier. • The thermistor RT has negative temperature coefficient. • Negative temparature coefficient means resistance decreases exponentially with increse in temparature T. EC302.30
7
Thermistor can be placed in any one of the two positions as shown in Fig Thermister RT is used to minimize the increase in collector current due to variations in ICO , VBE or β with temperature .
EC302.30
8
If the temparature increases •
Thermistor resistance decreases.
•
Current flowing through RT (IT) increases.
•
Since the voltage drop across RE increases in the direction, it reverse biases the transistor Base –Emitter
junction which reduces IBand keeps IC constant. •
Thus RT compensates the increase in IC due to temperature rise.
EC302.30
9
The process is as follows • Increases VE • Reduces VBE • VBE = VB - VE • VBE = VCC X R2 / (R1+R2) (fixed) • IB decreases • IC remains constant
EC302.30
10
• Thus the temperature sensitivity of RT provides compensation to the increase in collector current IC due to rise in temperature T. • The same result is obtained if the transistor RT is placed in the base circuit across R2 instead of in collector circuit.
EC302.30
11
SENSISTOR COMPENSATION
EC302.30
12
Sensistor compensation circuit Fig.1 EC302.30
13
•
Instead of thermistor compensation, compensation can be done by using sensistor.
•
Sensistor is a temperature sensitive device.
•
Sensistor has positive temperature coefficient.
•
Sensistor is a heavily doped semi conductor. EC302.30
14
Generally sensistors have
• Temperature coefficient of resistance of 0.007 per 0C
• The range of temperature from - 600 0C to 1500 0C.
EC302.30
15
•
The sensistor may be placed either in parallel with R1.
•
Or in parallel with RE
•
The sensistor can also be placed in place of RE rather than in parallel with RE. EC302.30
16
With the increase in temperature •
The resistance of RS increases.
•
So, the resistance of parallel combination (RS || R1) increases.
•
Hence voltage drop across R2 decreases.
•
VR2 = VCC*(R2 / (R1||RS) + R2)
EC302.30
17
•
Decrease in VR2 decreases the net forward emitter Bias (VBE).
•
Hence Collector current IC decreases.
EC302.30
18
•
Decrease in IC compensates the increase in collector current IC due to increase in IC0 ,β or VBE because of temperature rise.
EC302.30
19
Summary •
We have discussed the circuits using thermistors & sensistors.
•
The circuits stabilize IC against variations in ICO,β & VBE due to rise in temperature.
EC302.30
20
Quiz 1.
If the temperature increases, thermistor resistance A)
Increases
B)
Decreases
C) Constant D) Zero
EC302.30
21
•
In compensation the value IC must be A)
Decreased
B.
Increased
C) Constant D)
Zero
EC302.30
22
1.
If the temperature increase, sensistor resistance
A) Increases B) Decreases C) Constant D) Zero
EC302.30
23
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
•
Explain with circuit diagram the thermistor compensation?
•
Explain with circuit diagram the sensistor compensation?
EC302.30
24