Grid Training 6m34d
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 3b7i
Overview 3e4r5l
& View Grid Training as PDF for free.
More details w3441
- Words: 863
- Pages: 17
1
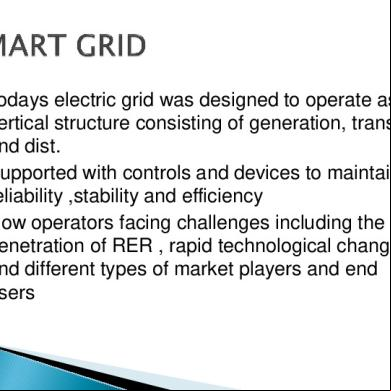
GRID TRAINING
Questions to spare a thought on…. 2
When your manager puts you in charge of organizing a project, what would you do first?
Would you develop the timelines and tasks and start to assign responsibility?
Would you think about other people and fit this into their tasks, opting for people who can and want to do it?
3
What would you do if tasks start to fall behind and the plan is off track?
Would you chase everyone to get back on track, regardless of other commitments they have?
Would you ease off, knowing that they are strained and just busy doing their jobs, let alone extra tasks you have given them?
Grid Training and Development 4
Proposed by Blake and Mouton
Also known as managerial grid
Aims at attaining much more than the development and growth of the individual managers
It is the technique which integrates individual, team and organizational development
5
This model depicts two prevailing concerns found in all organizations – concern for productivity and people
MG helps the managers in evaluating their concern for people and productivity.
It also stresses the importance of team – management leadership styles.
Stages of Managerial Grid 6
1) Training: The mangers learn about grid concepts and how they are applied in week long seminars. After appropriate instructions, these key managers will work to implement the grid programme through out the organization. 2) Team development: of the same department are brought together to discuss how they are going to attain 9, 9 position on the grid.
7
3) Intergroup development Marks the beginning of overall organizational development There is a shift from micro level of individual and group development to a macro level of group organizational development. The main focus is on improving co- ordination and cooperation among work groups Inter group tensions are dealt with openly and t problem solving procedures are adopted
8
4) Organizational goal setting The participants contribute to and agree up on the important goals of the organization. A sense of commitment and self control is instilled in the participants as the managers and subordinates work together through out the organization 5) Goal attainment The participants attempt to accomplish the goals which they set in the fourth stage.
9
6) Stabilization All the efforts from stage 1 to 5 are evaluated and critical analysis are made and in the light on this various programmes may be redesigned.
Interpretation of the leadership grid diagram
The Managerial Grid 10
Co-ordinates 11
Co-ordinates (1,1) – impoverished management The manager makes the minimum efforts to get required work accomplished as a result minimum standards of performance and minimum worker dedication
Co-ordinates(9,1) – Authority compliance Excellent work design efficiency in operations, well established procedures and the interference of human element is in the minimum degree.
12
Co-ordinates (1,9) – country club management
Thoughtful attention to the needs of the people Personal and meaningful relationship with workers, friendly atmosphere, high morale and loosely structured work design or in other words primary concern for people, production secondary
13
Co- ordinates (9,9) – (team Management) Work accomplishment from thoroughly committed people, trust worthy and respectful atmosphere, highly organized task performances
Co –ordinates (5,5) – middle of the road management - Concerned with balancing the necessity to get the work done while maintaining worker morale at a satisfactory level.
Behavioral elements 14
Grid theory breaks behavior down into seven key Description elements: Element Taking action, driving and ing Initiative Questioning, researching and ing Inquiry
understanding
Advocacy
Expressing convictions and championing ideas
Decision making
Evaluating resources, choices and consequences
Conflict resolution Resilience
Confronting and resolving disagreements
Critique
Delivering objective, candid
Dealing with problems, setbacks and failures
How to use the Model 15
Step 1: Identify your natural leadership style: Take the managerial grid questionnaire to see where you naturally fall within the grid
Step 2: Identify real world examples: - Now to your results of the questionnaire, think of an example in the real world where you had to handle a situation that involved leading someone or a team
- Plot this on the grid and see how you compared the questionnaire to the results
16
Step 3: Identify ways to improve: - With your managerial grid mapped, showing both the questionnaire results and the real world example, think about what you could improve to be a more ‘balanced’ leader, with the main target being team leader
Identify 3 ways to improve your skill set. Example: you may be too task oriented and therefore lack softer elements of people skills. Perhaps improving communication or delegation skills may help. Alternatively, you may be too people focused and perhaps some training on performance management would help you balance your skill set?
17
Step 4: Regularly reflect: Keep reflecting and reviewing your performances in situations. Take notes regularly and reflect every day or week, giving yourself an honest appraisal with the view of identifying how and where you can improve your skills
GRID TRAINING
Questions to spare a thought on…. 2
When your manager puts you in charge of organizing a project, what would you do first?
Would you develop the timelines and tasks and start to assign responsibility?
Would you think about other people and fit this into their tasks, opting for people who can and want to do it?
3
What would you do if tasks start to fall behind and the plan is off track?
Would you chase everyone to get back on track, regardless of other commitments they have?
Would you ease off, knowing that they are strained and just busy doing their jobs, let alone extra tasks you have given them?
Grid Training and Development 4
Proposed by Blake and Mouton
Also known as managerial grid
Aims at attaining much more than the development and growth of the individual managers
It is the technique which integrates individual, team and organizational development
5
This model depicts two prevailing concerns found in all organizations – concern for productivity and people
MG helps the managers in evaluating their concern for people and productivity.
It also stresses the importance of team – management leadership styles.
Stages of Managerial Grid 6
1) Training: The mangers learn about grid concepts and how they are applied in week long seminars. After appropriate instructions, these key managers will work to implement the grid programme through out the organization. 2) Team development: of the same department are brought together to discuss how they are going to attain 9, 9 position on the grid.
7
3) Intergroup development Marks the beginning of overall organizational development There is a shift from micro level of individual and group development to a macro level of group organizational development. The main focus is on improving co- ordination and cooperation among work groups Inter group tensions are dealt with openly and t problem solving procedures are adopted
8
4) Organizational goal setting The participants contribute to and agree up on the important goals of the organization. A sense of commitment and self control is instilled in the participants as the managers and subordinates work together through out the organization 5) Goal attainment The participants attempt to accomplish the goals which they set in the fourth stage.
9
6) Stabilization All the efforts from stage 1 to 5 are evaluated and critical analysis are made and in the light on this various programmes may be redesigned.
Interpretation of the leadership grid diagram
The Managerial Grid 10
Co-ordinates 11
Co-ordinates (1,1) – impoverished management The manager makes the minimum efforts to get required work accomplished as a result minimum standards of performance and minimum worker dedication
Co-ordinates(9,1) – Authority compliance Excellent work design efficiency in operations, well established procedures and the interference of human element is in the minimum degree.
12
Co-ordinates (1,9) – country club management
Thoughtful attention to the needs of the people Personal and meaningful relationship with workers, friendly atmosphere, high morale and loosely structured work design or in other words primary concern for people, production secondary
13
Co- ordinates (9,9) – (team Management) Work accomplishment from thoroughly committed people, trust worthy and respectful atmosphere, highly organized task performances
Co –ordinates (5,5) – middle of the road management - Concerned with balancing the necessity to get the work done while maintaining worker morale at a satisfactory level.
Behavioral elements 14
Grid theory breaks behavior down into seven key Description elements: Element Taking action, driving and ing Initiative Questioning, researching and ing Inquiry
understanding
Advocacy
Expressing convictions and championing ideas
Decision making
Evaluating resources, choices and consequences
Conflict resolution Resilience
Confronting and resolving disagreements
Critique
Delivering objective, candid
Dealing with problems, setbacks and failures
How to use the Model 15
Step 1: Identify your natural leadership style: Take the managerial grid questionnaire to see where you naturally fall within the grid
Step 2: Identify real world examples: - Now to your results of the questionnaire, think of an example in the real world where you had to handle a situation that involved leading someone or a team
- Plot this on the grid and see how you compared the questionnaire to the results
16
Step 3: Identify ways to improve: - With your managerial grid mapped, showing both the questionnaire results and the real world example, think about what you could improve to be a more ‘balanced’ leader, with the main target being team leader
Identify 3 ways to improve your skill set. Example: you may be too task oriented and therefore lack softer elements of people skills. Perhaps improving communication or delegation skills may help. Alternatively, you may be too people focused and perhaps some training on performance management would help you balance your skill set?
17
Step 4: Regularly reflect: Keep reflecting and reviewing your performances in situations. Take notes regularly and reflect every day or week, giving yourself an honest appraisal with the view of identifying how and where you can improve your skills